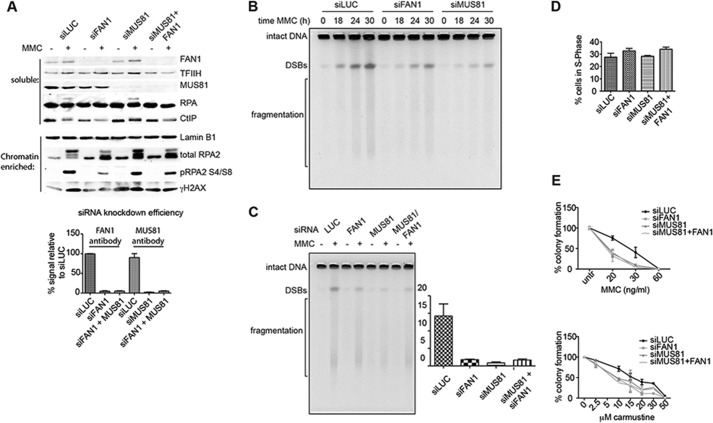
FIGURE 5.
FAN1- and/or MUS81-dependent DSB induction upon MMC treatment of human cells. A, top panel, FAN1 and/or MUS81 siRNA-mediated knockdown efficiencies assessed by Western blotting of total cell extracts of untreated (−) or MMC-treated (+) U2OS cells. TFIIH was used as a loading control. Quantification of the knockdown efficiencies shown in the bottom panel was carried out using ImageJ, and the graph was produced by GraphPad Prism (n = 3). The same extracts were probed for the markers of DSB metabolism RPA and CtIP. Center panel, Western blot analysis of the chromatin-enriched fraction of the above extracts probed for RPA, phospho-RPA, and γH2AX. Lamin was used as the loading control. B, time course of DSB formation assessed by pulsed field gel electrophoresis after MMC treatment (3 μg/ml) of U2OS cells, in which FAN1 or MUS81 were knocked down by siRNA. C, representative pulsed field gel electrophoresis image of DSBs induced by 24 h MMC (3 μg/ml) treatment of U2OS cells in which FAN1 and/or MUS81 were knocked down. The left panel shows a quantification of three independent experiments. siLUC was used as a control, and the ratio of DSBs of the MMC-treated samples divided by the untreated samples is shown for each siRNA condition. Error bars show mean ± S.E. D, quantifications of a FACS analysis of EdU-labeled cells pretreated with the indicated siRNAs and subsequently treated for 24 h with 3 μg/ml MMC. The knockdown did not affect cell viability during the course of the experiment. Error bars show mean ± S.E. (n = 3). E, clonogenic survival assay of U2OS cells treated with the indicated siRNAs and drugs. Colonies were counted 8 days after treatment, and MMC was washed out 24 h after treatment.