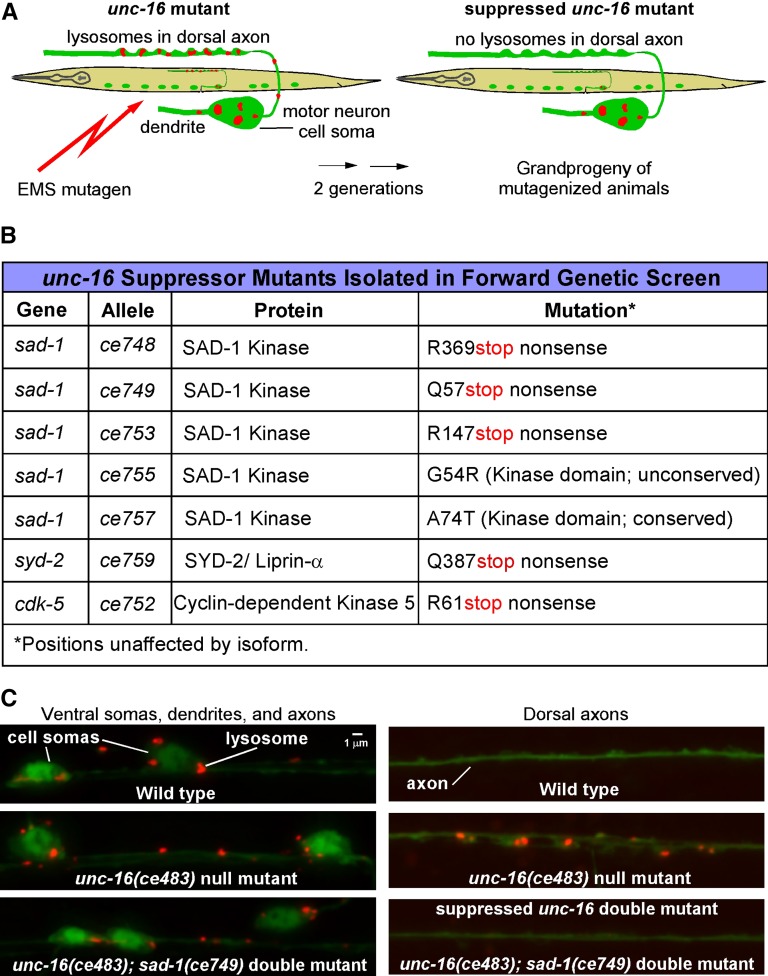
Figure 1.
Forward genetic screen for mutations that suppress axonal lysosome accumulation in unc-16 mutants. (A) Drawings illustrate the forward genetic screen for unc-16 suppressor mutants. The screen used EMS to mutagenize an unc-16 null mutant carrying the integrated transgene ceIs134, which uses the unc-17β promoter to co-express CTNS-1-RFP (to mark lysosomes) and GFP (as an expression control) in the ventral cord cholinergic motor neurons. We screened the F2 grandprogeny of mutagenized animals on 96-well glass-bottom Mat-Tek plates using an inverted microscope and selected animals with few or no lysosomes in their dorsal axons and normal GFP expression. (B) Summary of mutations identified in the unc-16 suppressor screen. “Conserved” means that the amino acid is conserved in the human ortholog of SAD-1, known as SAD-A/B or BRSK2. ce753 and ce755 are weaker suppressors of unc-16 than the sad-1 nonsense mutants, and they contain some lysosomes in their dorsal axons. (C) Representative images of wild-type, the unc-16 mutant, and a double mutant carrying the unc-16 null mutation in combination with one of the suppressor mutations. Lysosomes (red puncta) are inside GFP-labeled cholinergic motor neurons (green).