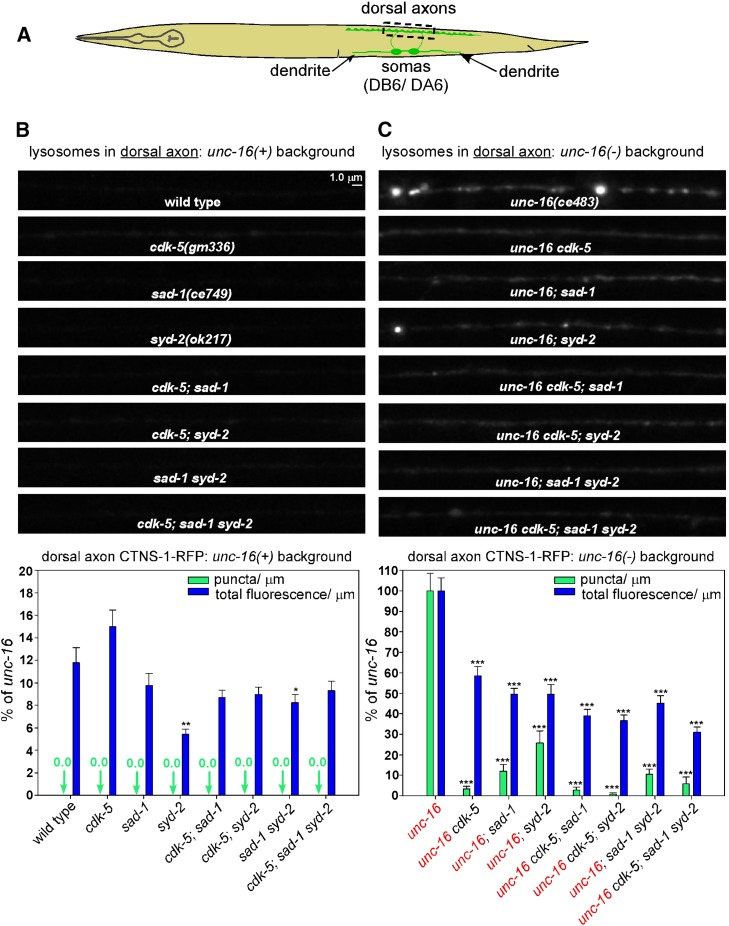
Figure 2.
CDK-5, SAD-1, and SYD-2 act together to promote axonal lysosome accumulation in an unc-16 null mutant. (A) Drawing illustrates the location and anatomy of the cholinergic motor neurons imaged in this figure. Dashed box outlines the region imaged. (B and C) Representative, identically scaled images and quantification of CTNS-1-RFP lysosomal puncta and total fluorescence per micrometer of the indicated genotypes in an unc-16(+) background (B) or an unc-16(−) background (C). CTNS-1-RFP is expressed from the integrated transgene ceIs56. Data are means and SEMs from 13–14 animals. Asterisks indicate values significantly different from wild type (B) or unc-16 (C): *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.0001. For lysosome punctal density in an unc-16(−) background, none of the CCS mutant combinations differed significantly from the component single mutants. However, for the fluorescence/μm parameter, the unc-16 cdk-5; sad-1 triple mutant and the unc-16 cdk-5; sad-1 syd-2 quadruple mutant showed small but significant reductions when compared to the unc-16; sad-1 double mutant (P = 0.02 and <0.0001), and the unc-16 cdk-5; syd-2 triple mutant showed a small but significant reduction when compared to unc-16; syd-2 (P = 0.03).