Abstract
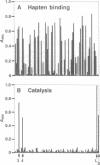
The low abundance and activity of catalytic antibodies are major obstacles to their selection from the virtually unlimited repertoire of antibody binding sites. The requirement for new screening methodologies is further emphasized by the availability of combinatorial libraries, in which a functional polypeptide has to be selected out of millions of possibilities. We present a simple and sensitive screening approach (termed catELISA) based on immobilized substrates and immunodetection of the end product of the catalyzed reaction. The feasibility of catELISA is demonstrated here by the generation of potent ester-hydrolyzing antibodies by direct screening of hybridoma supernatants. We show that this approach is not only facile but general: it is not limited by type of reaction, substrate, or catalyst (enzymes, catalytic antibodies, chemical catalysts). catELISA opens a route to catalytic antibodies that replaces existing lengthy and arduous methods, thus allowing us to expand their number and improve their quality and to address questions that would otherwise be difficult to answer.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benkovic S. J., Adams J. A., Borders C. L., Jr, Janda K. D., Lerner R. A. The enzymic nature of antibody catalysis: development of multistep kinetic processing. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1135–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2251500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran A. G., Schultz P. G. Antibody-catalyzed porphyrin metallation. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):781–783. doi: 10.1126/science.2389144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. S. Monoclonal antibodies as catalysts and templates for organic chemical reactions. Adv Biotechnol Processes. 1989;11:359–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huse W. D., Sastry L., Iverson S. A., Kang A. S., Alting-Mees M., Burton D. R., Benkovic S. J., Lerner R. A. Generation of a large combinatorial library of the immunoglobulin repertoire in phage lambda. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1275–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.2531466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson S. A., Sastry L., Huse W. D., Sorge J. A., Benkovic S. J., Lerner R. A. A combinatorial system for cloning and expressing the catalytic antibody repertoire in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54(Pt 1):273–281. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1989.054.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. R., Prudent J. R., Kochersperger L., Yonkovich S., Schultz P. G. An efficient antibody-catalyzed aminoacylation reaction. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):365–367. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A. Antibodies of predetermined specificity in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1984;36:1–44. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60898-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Benkovic S. J. Principles of antibody catalysis. Bioessays. 1988 Oct;9(4):107–112. doi: 10.1002/bies.950090402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Benkovic S. J., Schultz P. G. At the crossroads of chemistry and immunology: catalytic antibodies. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):659–667. doi: 10.1126/science.2024118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. T., Napper A. D., Schultz P. G., Rees A. R. Mechanistic studies of a tyrosine-dependent catalytic antibody. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9757–9761. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S., Johnson D. R., Massey R. Binding and multiple hydrolytic sites in epitopes recognized by catalytic anti-peptide antibodies. Ciba Found Symp. 1991;159:156–173. doi: 10.1002/9780470514108.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S., Volle D. J., Beach C. M., Johnson D. R., Powell M. J., Massey R. J. Catalytic hydrolysis of vasoactive intestinal peptide by human autoantibody. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1158–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.2727702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawfik D. S., Green B. S., Eshhar Z. Detection of catalytic monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1992 Apr;202(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90201-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawfik D. S., Zemel R. R., Arad-Yellin R., Green B. S., Eshhar Z. Simple method for selecting catalytic monoclonal antibodies that exhibit turnover and specificity. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 23;29(42):9916–9921. doi: 10.1021/bi00494a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Milstein C. Man-made antibodies. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):293–299. doi: 10.1038/349293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]