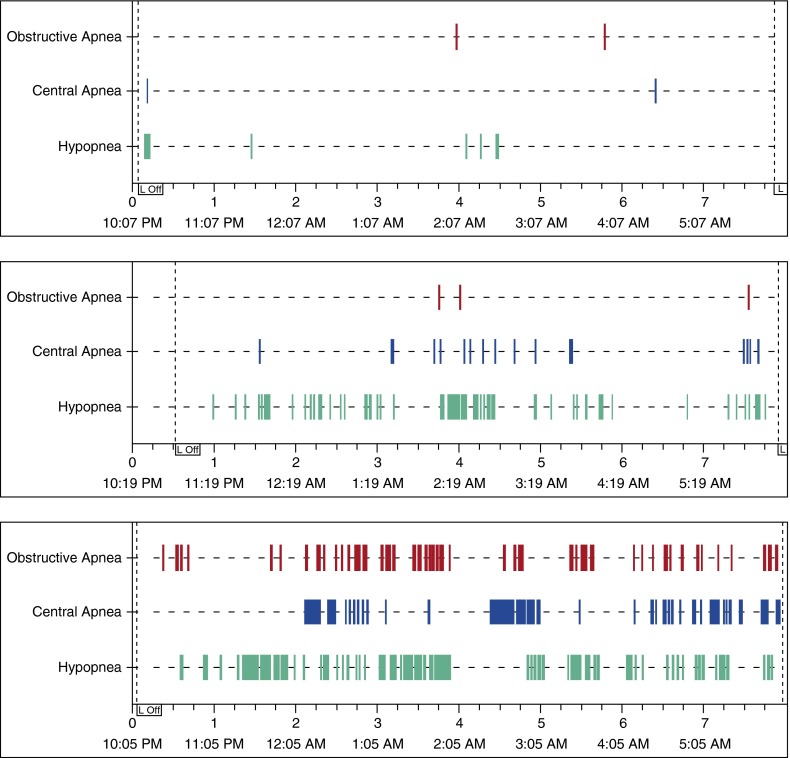
Figure 3.
Polysomnography data from a representative participant studied on 10 cm H2O positive airway pressure (PAP) at 1,320 m (top) and at 2,750 m (middle). The participant was also studied at 2,750 m without PAP (bottom). Sleep apnea appears well controlled at 1,320 m, but not at 2,750 m. At 2,750 m, application of PAP resulted in fewer central apnea events as well as fewer obstructive apnea events. For all three studies, the participant did not receive supplemental oxygen. L Off = lights off.