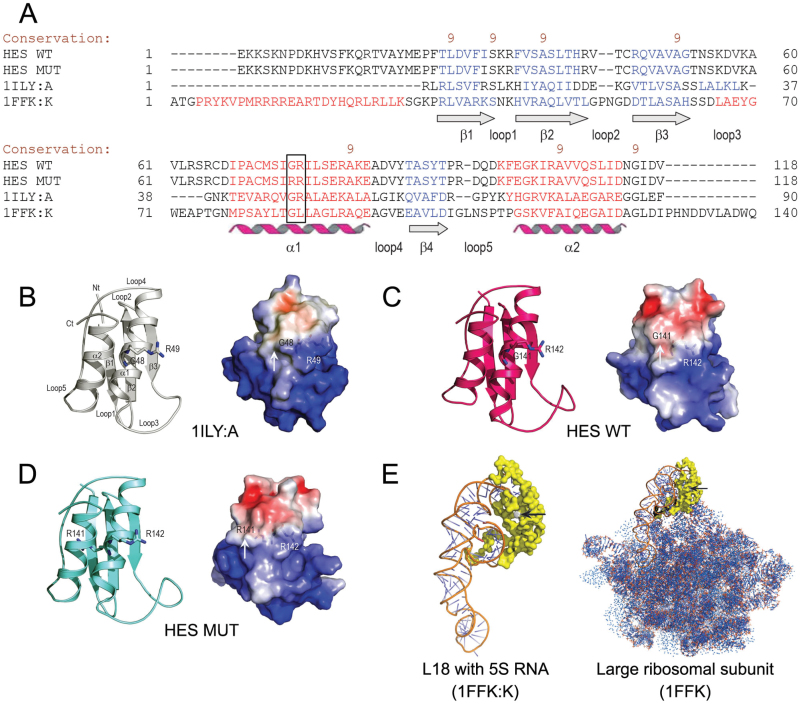
Fig. 6.
3D molecular models of HES proteins. (A) A sequence alignment of the Arabidopsis HES wild-type (WT) and G141R mutant (MUT) proteins, the L18 ribosomal protein from T. thermophiles (PDB accession 1ILY:A), and the L18 ribosomal protein from H. marismortui (PDB accession 1FFK:K) by PROMALS3D (Pei et al., 2008). The black box indicates the GR/RR motif in the HES proteins and the corresponding regions in 1ILY:A and 1FKK:K. The degree of conservation of amino acid residues is shown by brown numbers on the scale 9-5. The secondary structures are indicated in blue (β-sheets 1–4) and red (α-helices 1 and 2). The adjoining loops are also indicated (cf. Fig. 6B). (B-D) 3D structure of the T. thermophiles L18 protein (B), and molecular models of the Arabidopsis HES wild-type (C) and G141R mutant proteins (D). The NH2-terminus (Nt) and COOH-terminus (Ct) are indicated alongside the secondary structural elements in the top left part of panel B. The G48 and R49, G141 and R142, and R141 and R142 residues in the 1ILY:A, and the HES wild-type, and mutant proteins are shown in sticks. The right panels illustrate molecular surface morphologies coded by electrostatic potentials. White, blue, and red patches on protein surfaces indicate electro-neutral, electropositive (5 kT/e), and electronegative patches (-5 kT/e) respectively. In the G141R mutant, an additional bulge is present on its surface (cf. white arrows in all three right panels). The residues of the GR and RR motifs in the wild-type and mutant proteins are illustrated by sticks and are visible under the molecular surfaces. (E) The 3D structure of the L18 ribosomal protein from H. marismortui (1FFK:K) with 5S rRNA bound (left panel). The right panel shows the 3D structure of the large (50S) ribosomal subunit (1FFK). The black arrows point to the GL region in 1FFK:K and 1FFK that corresponds to GR and RR regions in the Arabidopsis HES proteins (cf. Fig. 6A).