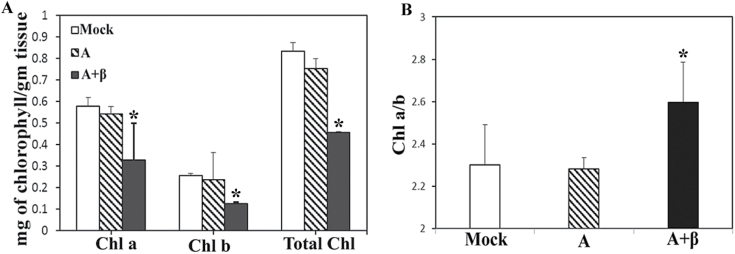
Fig. 2.
RaLCB infection causes degradation of chlorophyll in N. benthamiana. (A) Relative amount of chlorophyll a (mg g–1), chlorophyll b (mg g–1), and total chlorophyll (mg g–1) and (B) the chlorophyll a/b ratio from leaves of mock- (control), A-, and A+β-inoculated plants at 28 dpi. Each bar represents a grand mean ±SD of three experimental means. The chlorophyll concentration determinations were carried out for three biological and three technical replicates (a total of nine replicates) and the grand means of values for chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, total chlorophyll and the chlorophyll a/b ratio were calculated and subjected to analysis of variance followed by post-hoc Scheffe test to determine significant differences between mock-, A-, and A+β-infected samples at the 0.05 significance level. Bars marked with an asterisk (*) represent samples showing a significant difference in level.