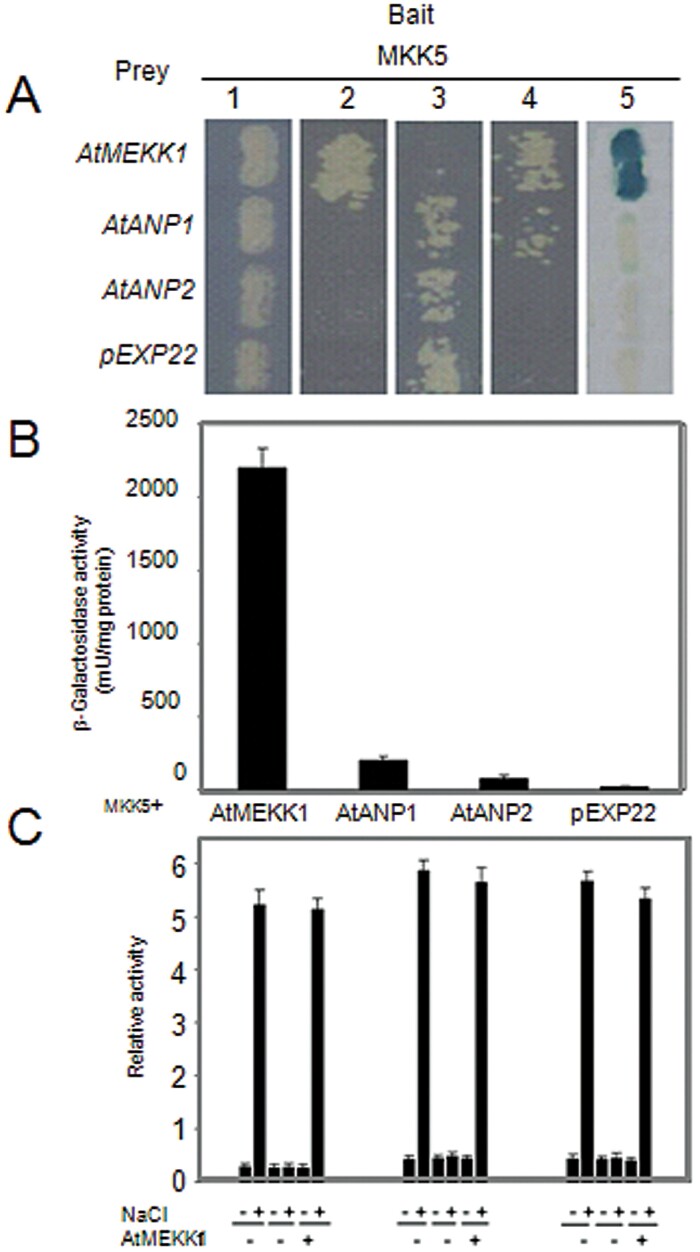
Fig. 6.
MKK5 specifically interacts with MEKK1. (A) MKK5 strongly interacted with MEKK1 in the yeast two-hybrid system. Yeast strains containing pEXPTM32-MKK5 as bait and pEXPTM22-MEKK1 as prey were grown on the following medium to screen for transformants: 1, SC medium lacking Leu and Trp for 48h; 2, SC medium lacking Leu, Trp, and Ura for an additional 48h to select the transformants; 3, SC medium lacking Leu and Trp and adding 0.2% of 5-fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA) for an additional 48h to select the cells containing interacting proteins; 4, SC medium lacking Leu, Trp, and His and adding 100mM 3-Amino-1,2,4-Triazole (3AT) for an additional 48h to confirm the interaction; 5, YPAD medium 48h, then an X-Gal assay was performed on the membrane to confirm the results. The pEXPTM22 empty prey vector was used as negative control. (B) Quantitative analysis of -galactosidase activity of the yeast strains in liquid culture showing the interaction between MKK5 and MEKK1. Values are means of data from at least three independent experiments. (C) Relative GUS activity driven by MKK5, FSD2, or FSD3 promoters, respectively, showed the response to NaCl in transiently transfected protoplasts of wild-type (M) or mekk1 (m) plants. The MEKK1 genes were cloned and co-transformed into protoplasts of the mekk1 mutant. All experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results.