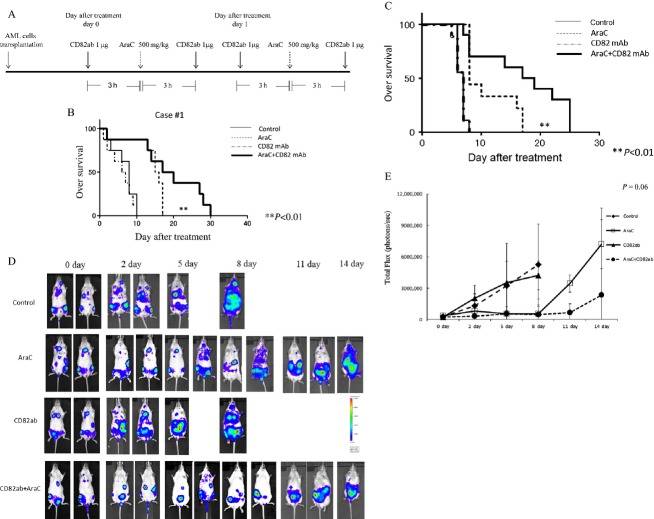
Figure 2.
The effect of CD82 monoclonal antibody (CD82 mAb) and AraC on overall survival of human AML-bearing mice. Treatment schedule: (A) NOD.Cg-Rag1tm1Mom Il2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NRG) mice-bearing human AML cells were treated with either AraC (500 mg/kg, on days 0 and 1) and/or CD82 mAb (1 μg, twice a day, on days 0 and 1). The control mice received isotype control IgG. Kaplan–Meier plot of survival of leukemic mice. (B and C) NRG mice were intravenously injected with AML (case 1) cells isolated from a patient or MOLM13 cells. The NRG mice-bearing human AML cells were treated by intravenous administration of either isotype control IgG (n = 8), CD82 mAb alone (n = 8), AraC alone (n = 8), or the combination of CD82 mAb and AraC (n = 8). Statistical significance was assessed by log-rank test. **P < 0.01. Bioluminescence imaging (BLI). (D) MOLM13 cells transduced with MSCV-GFP-T2A-Luciferase lenti-reporter vector were intravenously injected into NRG mice via the tail vein. After 3 weeks, isotype control IgG, CD82 mAb, and/or AraC (n = 8) were intravenously injected into MOLM13-bearing NRG mice. Leukemic cell burden was assessed by d-luciferin injection at several time points. One representative animal from each group is shown over time. Photon flux is indicated in the color scale bar. (E) Quantitative analysis of whole-body BLI. Each bar represents the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison tests.