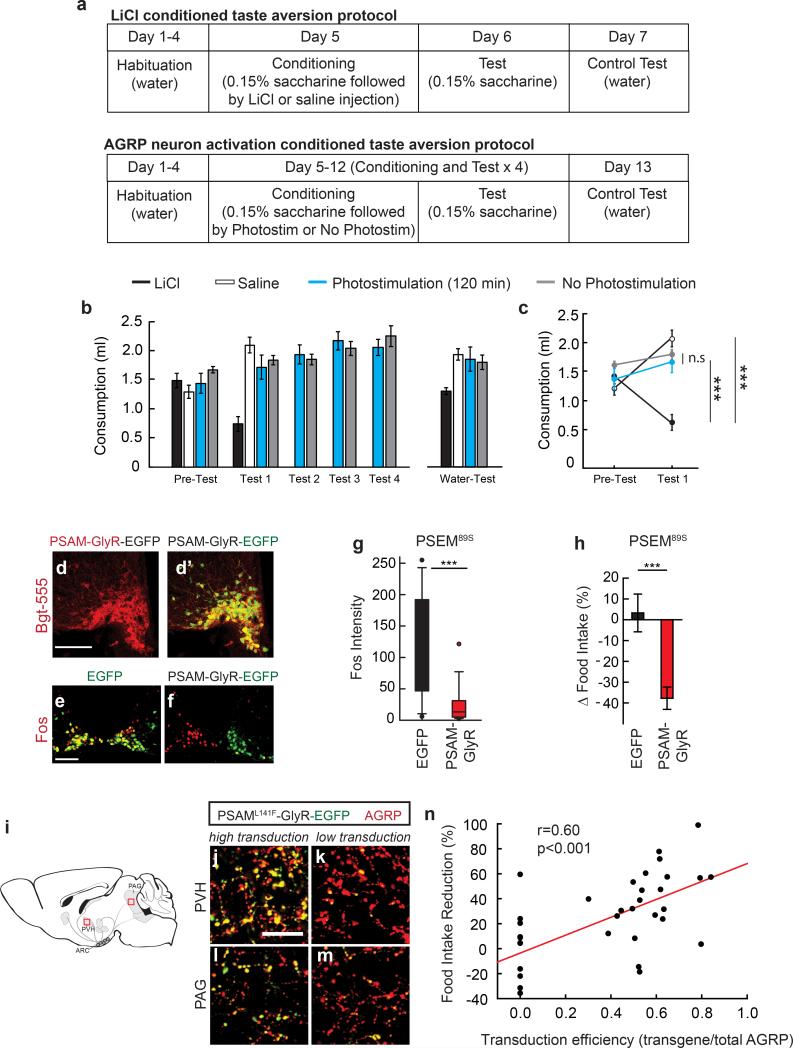
Extended Data Figure 2. AGRP neuron activation does not condition taste aversion, and feeding reduction correlates with proportion of AGRP neurons inhibited.
a, Experimental design for conditioned taste aversion experiments. Mice were water restricted and habituated to drink water from a spout during 20 min sessions. Four groups of mice were then allowed to consume a tastant (0.15% saccharine solution) for 20 min (Pre-Test) and immediately following this session, they were exposed to a conditioning agent (LiCl, saline, 120-min AGRP neuron photostimulation, or AGRPChR2 mice attached to an optical fibre but not phostostimulated; all n=6 mice). The next day, mice were tested for consumption of the saccharine solution (Test 1). For AGRP neuron photostimulated and non-photostimulated groups, conditioning and testing was extended with an additional three conditioning and test sessions. The day following the last testing session for each group, water consumption was also measured (Water-Test). b,c, Consumption of tastant solution for all sessions (b) and comparison for Pre-Test and Test 1 session (c). d,d’, Confocal micrographs of Cre recombinase-expressing AGRP neurons transduced with rAAV-Syn-FLEX-PSAML141F-GlyR-IRES-EGFP. Alexa555-conjugated-Bungarotoxin (Bgt-555) labels PSAML141F-GlyR (d), which co-localizes with EGFP (d’). Scale, 100 μm. e,f, Fos immunofluorescence in the ARC of mice treated with PSEM89S during the first 4 hours of the dark period without access to food. AGRPEGFP mice (e) show high levels of Fos in AGRP neurons and AGRPPSAM-GlyR mice (f) express low levels of Fos in neurons that express PSAM-GlyR (right side); non-transduced neurons (contralateral side) express high levels of Fos. Scale, 100 μm. g, Fos immunofluorescence intensity in AGRP neurons from AGRPPSAM-GlyR or AGRPEGFP mice after PSEM89S treatment during the first 4 hours of the dark period without access to food (n=3 mice/condition, n>50 nuclei/condition). h, Change in food intake for AGRPEGFP mice (n = 12) or AGRPPSAM-GlyR mice (n = 23) treated with PSEM89S during the first 4 hours of the dark period relative to saline injected on successive days. i, Diagram of AGRP neuron axon projection fields showing from from where transduction efficiency was calculated. i-m, After rAAV-hSyn-FLEX-rev-PSAML141F-GlyR-IRES-EGFP transduction of Agrp-IRES-Cre mice, measurement of EGFP transduction efficiency in AGRP boutons in the PVH (i,k) and PAG (l,m). High transduction efficiency (>50% in AGRP boutons) is shown (i,l) in comparison to low transduction efficiency (<50% in AGRP boutons) (k,m). Scale, 20 μm. n, Food intake reduction for mice treated with PSEM89S is correlated with the transduction efficiency of rAAV-hSyn-FLEX-rev-PSAML141F-GlyR-IRES-EGFP in AGRP neurons (EGFP transduced boutons/total AGRP boutons) (n=35 mice). n.s. p>0.05, ***p<0.001. Values are means ± s.e.m.