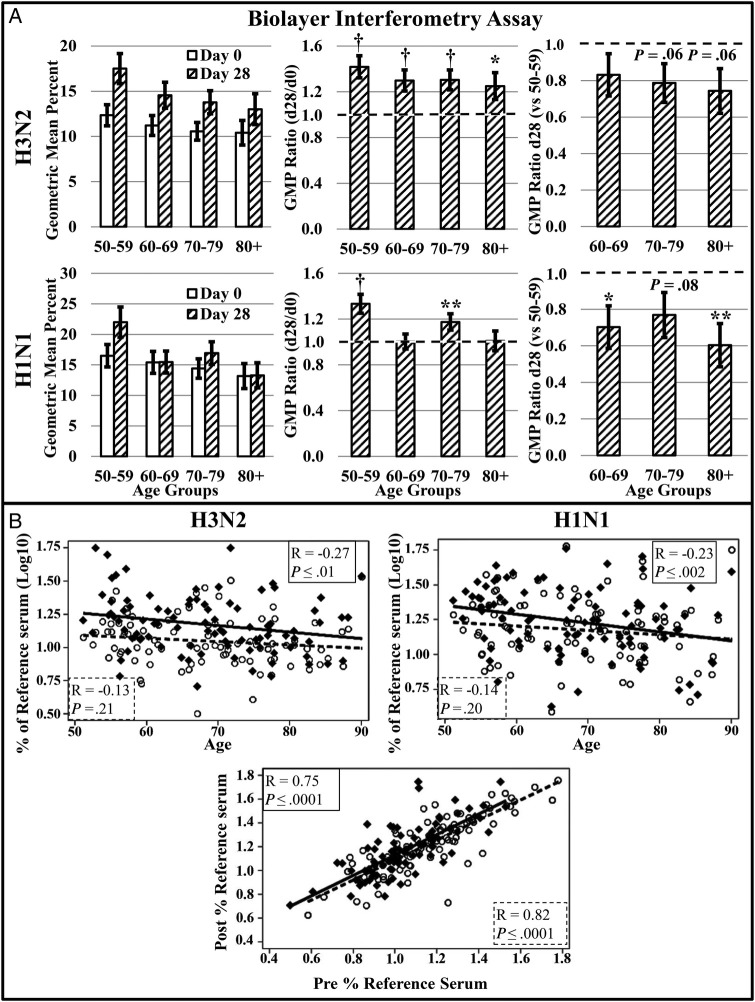
Figure 2.
Assessment of antibody binding capacity by biolayer interferometry. A, Antibody binding capacity (n = 90) to H3N2 and H1N1 was assessed on day 0 prior to vaccination and day 28 after vaccination. The geometric mean percent (GMP) ratio (day 28 GMP/day 0 GMP) was calculated to determine the vaccine-associated change in antibody binding within each age group. A GMP ratio of 1 (dotted line) is indicative of no change. Day 28 GMP ratios were used to compare responses of older adult groups to middle-aged controls (day 28 GMP of older adult group/day 28 GMP of 50–59 age group). A GMT ratio less than 1 (dotted line) is indicative of lower postvaccination antibody binding. B, Antibody binding capacity was plotted by age and correlations calculated to determine the effect of age on preexisting ( ) and postvaccination antibody binding (
) and postvaccination antibody binding ( ). The correlation coefficient and P value are presented for preexisting (
). The correlation coefficient and P value are presented for preexisting ( ) and postvaccination (
) and postvaccination ( ) correlations with age. The influence of preexisting, cross-reactive antibody on the day 28 postvaccination response to H1N1 (
) correlations with age. The influence of preexisting, cross-reactive antibody on the day 28 postvaccination response to H1N1 ( ) and H3N2 (
) and H3N2 ( ) was also determined. The correlation of pre- and postvaccination antibody responses to H1N1 (
) was also determined. The correlation of pre- and postvaccination antibody responses to H1N1 ( ) and H3N2 (
) and H3N2 ( ) are depicted. The correlation coefficient and P value are presented for prevaccination H1N1 (
) are depicted. The correlation coefficient and P value are presented for prevaccination H1N1 ( ) and H3N2 (
) and H3N2 ( ) correlations with the postvaccination antibody binding capacity. Error bars represent 1 standard error. Significance is indicated by *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01, †P ≤ .001.
) correlations with the postvaccination antibody binding capacity. Error bars represent 1 standard error. Significance is indicated by *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01, †P ≤ .001.