Fig. 2.
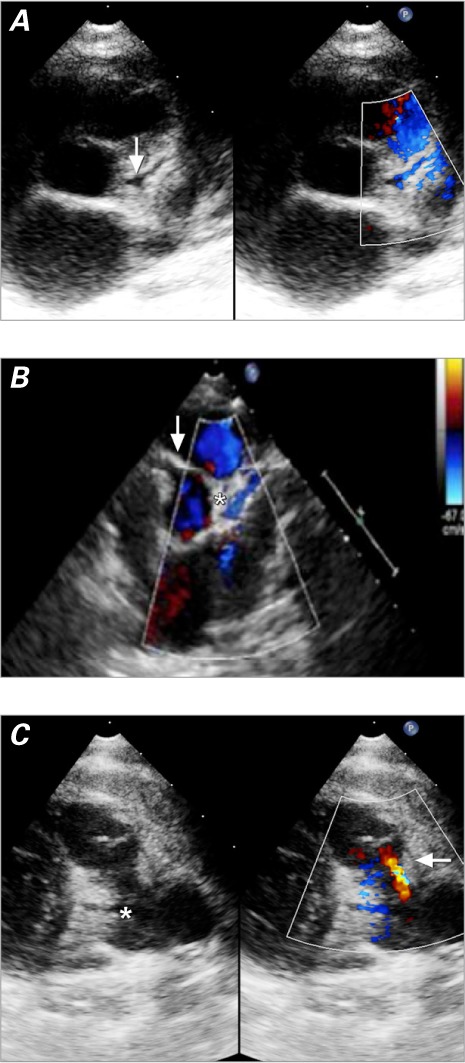
Two-dimensional echocardiograms. A) Patient 6. The parasternal short-axis view gives the erroneous impression that the left coronary artery emerges from the aortic root (arrow). In color-flow Doppler mode, diastolic flow from right to left (in blue) is seen inside the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. B) Patient 10. The parasternal short-axis view shows that the left coronary artery has no connection to the aorta despite their proximity and has retrograde diastolic flow (in blue) from right to left (asterisk). The dilated right coronary artery emerges from the aortic root (arrow). C) Patient 4. The parasternal short-axis view shows retrograde diastolic flow in the main pulmonary artery from the left coronary artery (in red) from left to right (arrow). The origin of the left coronary artery from the main pulmonary artery (asterisk) should not be mistaken for a persistent ductus arteriosus.
