Figure 1.
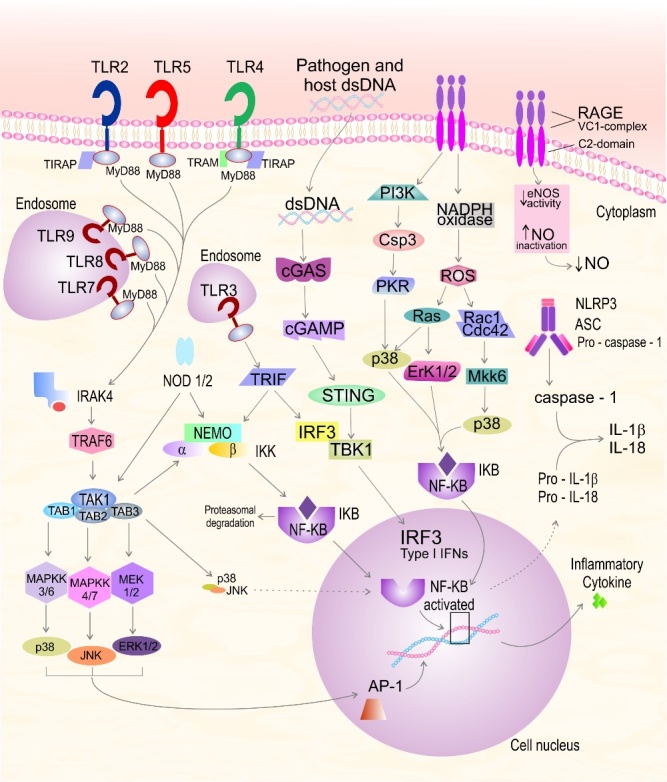
Recognition of pathogens by the innate immune system. Toll-like receptors (TLR) recognize molecular motifs that are expressed by pathogens or endogenous ligands released from damaged cells. AGE, advanced glycation end products; AP-1, activator protein-1; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase-recruitment domain; Cdc42, cell division control protein 42 homolog; Csp3, caspase-3; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ERK, extracellular signal regulated; IL, interleukin; IKK, NEMO/IKKα/IKKß complex; IRAK-4, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4; IκB, inhibitor of NF-κB; IKK, IκB kinase; INF, interferon; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; JNK, c-jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinases; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MKK, MAPK kinase; NADPH, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NEMO, NF-κB essential modulator, IKKγ; NF-κB, nuclear transcription factor kappa B; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat protein 3; NO, nitric oxide; NODs, nucleotide binding oligomerisation domains; PI3K, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; PKB, protein kinase A; RAGE; receptor for advanced glycation endproducts; PKR, protein kinase RNA-activated; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TAB, TGF-β-activated kinase 1-binding protein 1; TAK1, TGFß activated kinase 1; TIRAP, TIR-containing protein; TLRs, toll-like receptors; TRAF, receptor-associated factor; TRAM, TRIF-related adaptor molecule; TRIF, TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β
