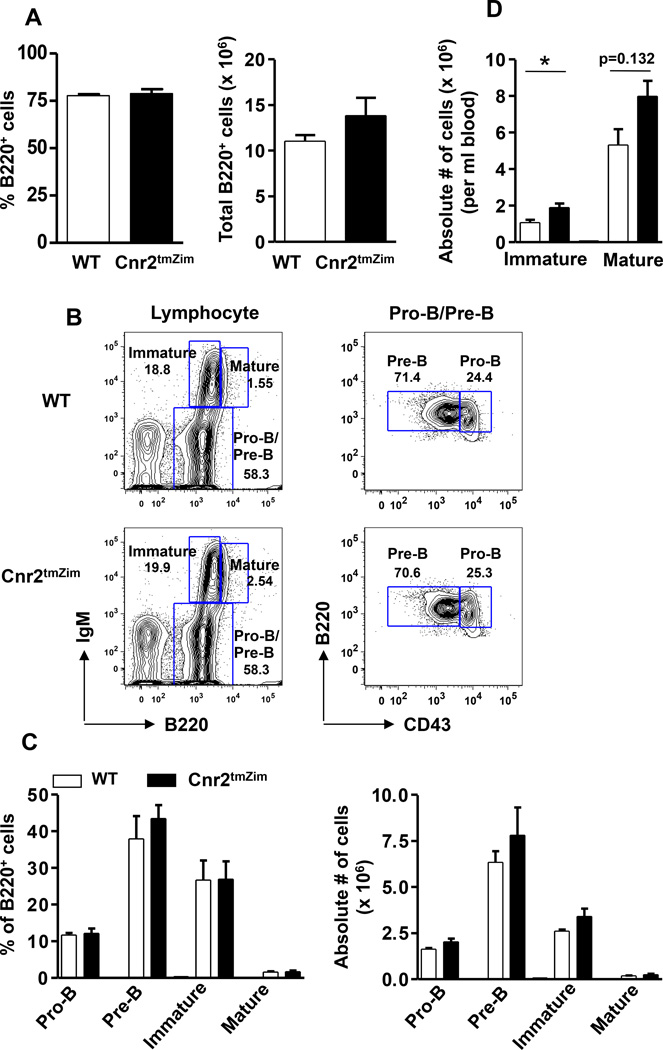
Figure 6. CB2 is dispensable for the early B cell development in the BM and in its absence immature B cells are more prevalent in the peripheral blood.
(A) BM cells from WT (open bar) and Cnr2tmZim (closed bar) mice were isolated from the left femur and tibia, stained with anti-B220, and analyzed by flow cytometry. For the determination of cellularity, RBC-depleted BM cells were counted with Turk’s solution. The percentage (left panel) and absolute number (right panel) of total B cells from WT and CB2−/− mice are indicated. Data are the mean ± SEM from 2 independent experiments with 3 mice per group. (B, C) BM cells from WT and Cnr2tmZim mice were stained with monoclonal antibodies specific to B220, IgM, and CD43 to identify Pro B (B220+IgM−CD43+), Pre B (B220+IgM−CD43−), immature (B220intIgM+), and mature (B220hiIgM+) B cells by flow cytometry. (B) Representative contour plots show relative frequencies of Pro B/Pre B, immature and mature B cells (left panel), and pro B and Pre B cells separately (right panel) from WT (top panel) and Cnr2tmZim (bottom panel) mice. Numbers on the plots represent the percentage of cells in the corresponding gate. (C) The cumulative percentages (left panel) and absolute numbers (right panel) of the indicated B cell subsets from WT (open bar) and Cnr2tmZim (closed bar) mice are shown. Data are the mean ± SEM from 2 independent experiments with 3 mice per group. (D) Peripheral blood from WT (open bar) and Cnr2tmZim (closed bar) mice was stained with monoclonal antibodies against B220 and CD93 to identify mature/recirculating (B220+CD93−) and immature (B220+CD93+) and B cells. For the determination of absolute cell numbers, blood counts were performed using a Heska ABC animal cell counter. Data are the mean ± SEM from 2 independent experiments with 3 mice per group. *p<0.05.