Figure 3.
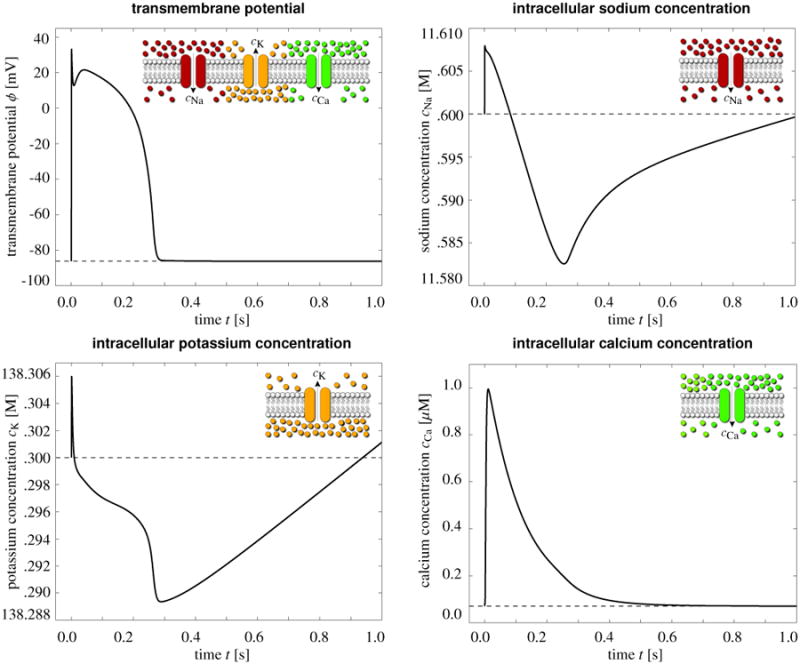
Electrochemistry in a human ventricular cardiomyocyte. Temporal evolution of the transmembrane potential ϕ and of the intracellular sodium potassium and calcium concentrations cCa, cK, and cCa. The influx of positively charged sodium ions generates a rapid upstroke in the transmembrane potential. At peak, the efflux of positively charged potassium ions initiates an early, partial repolarization. During the plateau, the influx of positively charged calcium ions balances the efflux of positively charged potassium ions. Final repolarization begins when the efflux of potassium ions exceeds the influx of calcium ions. Throughout the interval between the end of repolarization and the beginning of the next cycle, the cell is at rest.
