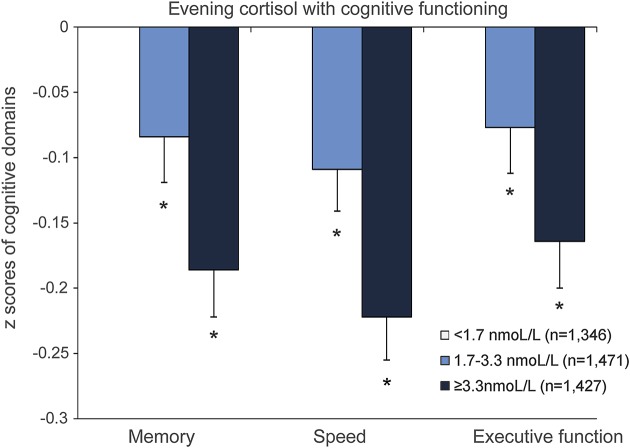
Figure 2. Adjusted mean cognitive domain z scores according to tertiles of evening cortisol.
Cognitive scores are adjusted for age, sex, educational level, current smoking status, alcohol intake, any steroid use, depressive symptoms, body mass index, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, and physical activity. *Significantly (p < 0.05) different from lowest tertile of evening cortisol (reference value = 0, not visible in figure). Adjusted mean z score differences for memory: middle vs lowest tertile −0.084 (95% confidence interval [CI] −0.152 to −0.015); highest vs lowest tertile −0.186 (95% CI −0.256 to −0.116); for speed: middle vs lowest tertile −0.109 (95% CI −0.172 to −0.045); highest vs lowest tertile −0.222 (95% CI −0.288 to −0.157); and for executive functioning: middle vs lowest tertile −0.077 (95% CI −0.145 to −0.009); highest vs lowest tertile −0.164 (95% CI −0.235 to −0.094).