Fig. 6. Treatment with AMP peptide reverses LPS-induced disruption of occludin, ZO-1, and perijunctional actin in mouse jejunum mucosal tissue.
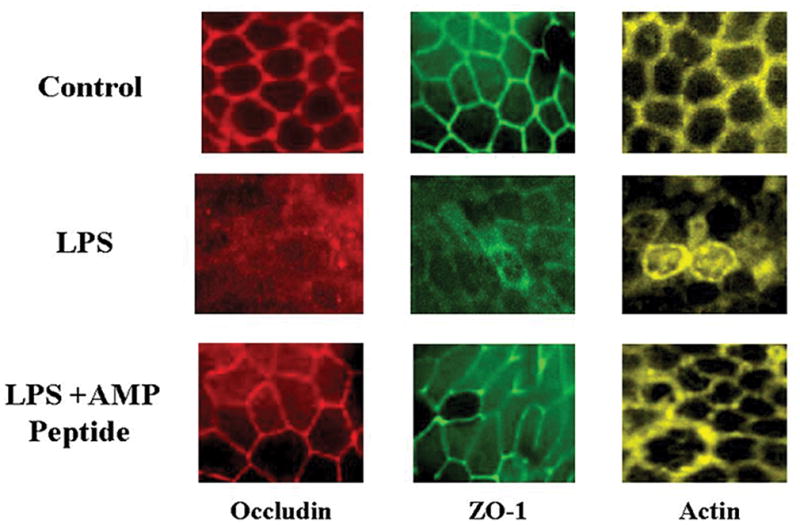
Tissue from mice with LPS-induced gut hyperpermeability were mounted on coverslips and subjected to IHC staining and LSCM. Tissue was taken for study 6 hr after administration of LPS; 21 hr after the experiment was initiated. Localization of occludin, ZO-1, and perijunctional actin in jejunum mucosal tissue from control animals is displayed from left to right in the top panels. Exposure to LPS disrupted TJs and diminished the amount of occludin (red), ZO-1 (green), and perijunctional actin (yellow) (middle panels). Treatment with AMP peptide restored the physiological distribution of occludin, ZO-1, and perijunctional actin in mice given LPS (bottom panels). Displayed are maximal projections of 5-μm Z-stacks through the area of TJs.
