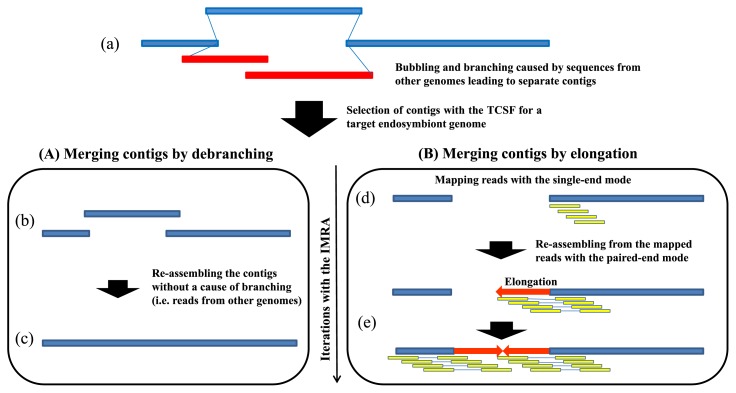
Fig. 5.
A schematic view of the improved genomic-sequence assembly following the use of TCSF and IMRA procedures in the strategy developed in this study. (a) A genomic sequence separated into contigs as a result of the path branching caused by sequences derived from other genomes. (b) A set of contigs obtained after removing contigs derived from other genomes. (c) Sequences merged into a contig by reassembling only reads that aligned onto the contigs. (d) Mapping reads onto contigs featuring a gap between them by using the single-end mode. (e) Elongating the contig ends by reassembling the mapped reads to make their unmapped-ends join the contig; the iterations of such an elongation close the gap.