Fig. 4.
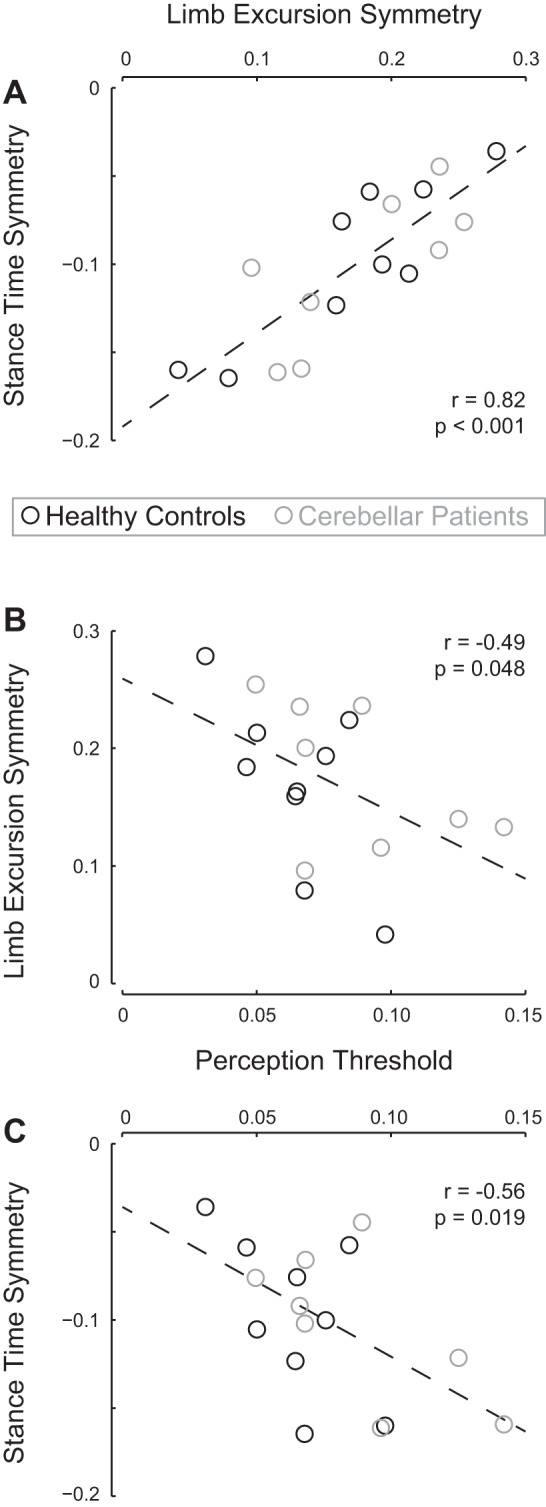
Observed relationships between speed-difference perception, stance time symmetry, and limb excursion symmetry during split-belt walking. A: stance time symmetry and limb excursion symmetry were significantly correlated, as was to be expected based on their mutual coupling to belt speed. Dashed line represents the linear regression line (y = 0.53x − 0.19). B: limb excursion symmetry was negatively correlated to perception threshold. Participants better able to perceive belt speed differences (low threshold) walk with less symmetric limb excursions. Dashed line represents the linear regression line (y = −1.33x + 0.26). C: stance time symmetry was negatively correlated to perception threshold. Participants better able to perceive belt speed differences (low threshold) walk with more symmetric relative stance times. Dashed line represents the linear regression line (y = −0.85x − 0.04). Values for patients are presented in gray and those for healthy controls in black.
