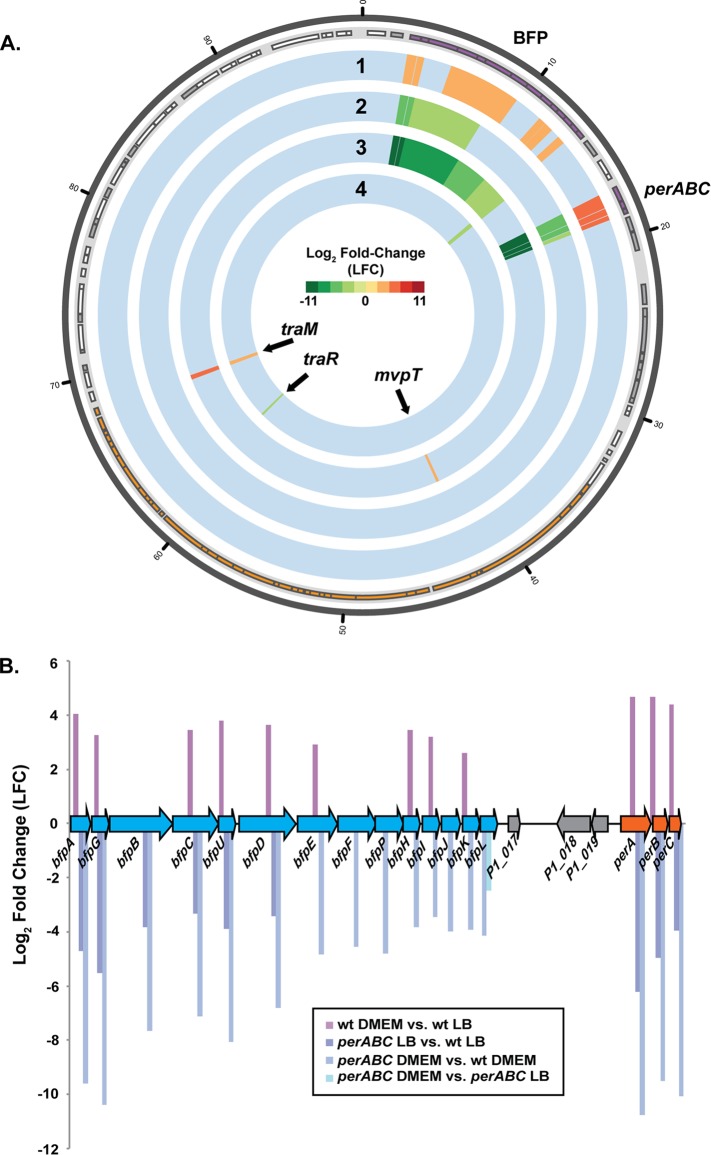
FIG 6.
RNA-Seq analysis of the global transcription of the E2348/69 EAF plasmid pMAR2. (A) Circular display of the differential expression analysis of genes on the EAF plasmid pMAR2 (22). RNA-Seq was used to determine changes in the global transcription of wild-type E2348/69, an E2348/69 ΔperABC mutant, and JPN15. The color scale indicates log2 fold change (LFC) from −11 (green) to 11 (red). The outermost track denotes the location of the protein-encoding genes and pseudogenes (22). Genes are indicated in the light gray outer track of the plot as rectangles of different sizes according to their coordinates and are colored purple to indicate BFP-associated genes, orange to indicate the conjugal transfer region, white to indicate protein-encoding genes, and gray to indicate pseudogenes. The tracks of differential expression data are as follows, from the outer track to the innermost track: wild-type E2348/69 in DMEM versus wild-type E2348/69 in LB (track 1), the ΔperABC mutant in LB versus wild-type E2348/69 LB (track 2), the ΔperABC mutant in DMEM versus wild-type E2348/69 in DMEM (track 3), and the ΔperABC mutant in DMEM versus the ΔperABC mutant in LB (track 4). (B) Diagram of the pMAR2 BFP operon and the LFC values of each gene in the BFP operon. The approximate size of each gene and the coding strand location are indicated by the size and orientation of the arrows. Genes identified in blue are involved in pilus biogenesis, while orange indicates the plasmid-encoded regulator genes, and gray indicates genes that encode hypothetical proteins.