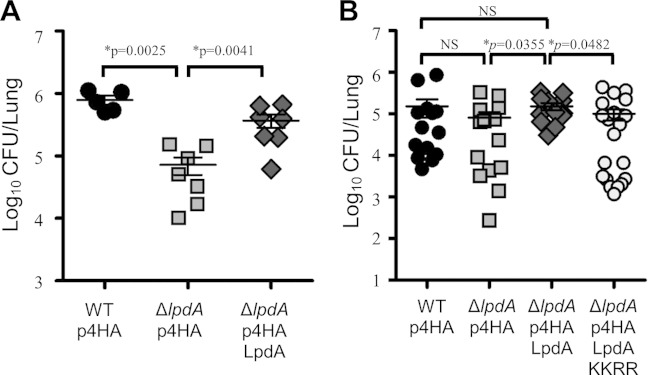
FIG 8.
LpdA contributes to the fitness of L. pneumophila 130b during pulmonary infections of A/J mice. The results of two independent experiments (A and B) are shown. A/J mice were infected with L. pneumophila wild-type (WT) and ΔlpdA mutant strains by intranasal inoculation. At 72 h postinfection, the animals were sacrificed and the CFU in the lungs determined by plating. (A) Both the wild type and the complemented ΔlpdA strain grew significantly (P = 0.0025 and P = 0.0041, respectively [Mann-Whitney U test]) better than the mutant strain in the lungs of mice. (B) The ΔlpdA strain and the ΔlpdA strain expressing the inactive LpdA KK165/376RR (KKRR) mutant are significantly (P = 0.0355 and P = 0.0482, respectively [Mann-Whitney U test]) attenuated compared to the complemented L. pneumophila ΔlpdA p4HA LpdA strain.