FIG 3.
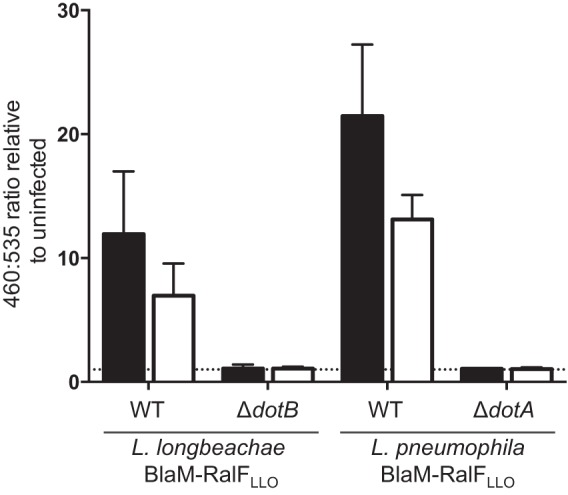
L. longbeachae Dot/Icm-dependent protein translocation occurs in the absence of host cell uptake. L. longbeachae and L. pneumophila strains expressing BlaM-RalFLLO were used to infect THP-1 cells that were treated with 20 μM cytochalasin D (white bars) or the equivalent volume of the carrier dimethyl sulfoxide (black bars) at an MOI of 40 for 1 h before the BlaM substrate CCF2-AM was added and translocation was measured using a fluorescence plate reader. Cells were excited at 415 nm, and the 460 nm/535 nm emission ratio was calculated relative to the ratio in uninfected cells. The mean ratio ± standard deviation is presented from at least three independent experiments. There is a statistically significant difference between the 460 nm/535 nm ratio of cells infected with L. longbeachae wild type (WT) and that of L. pneumophila wild type with cytochalasin D treatment (unpaired, two-tailed t test; P = 0.031). The dotted line represents a fluorescence ratio of 1, a value equivalent to that of an uninfected sample.
