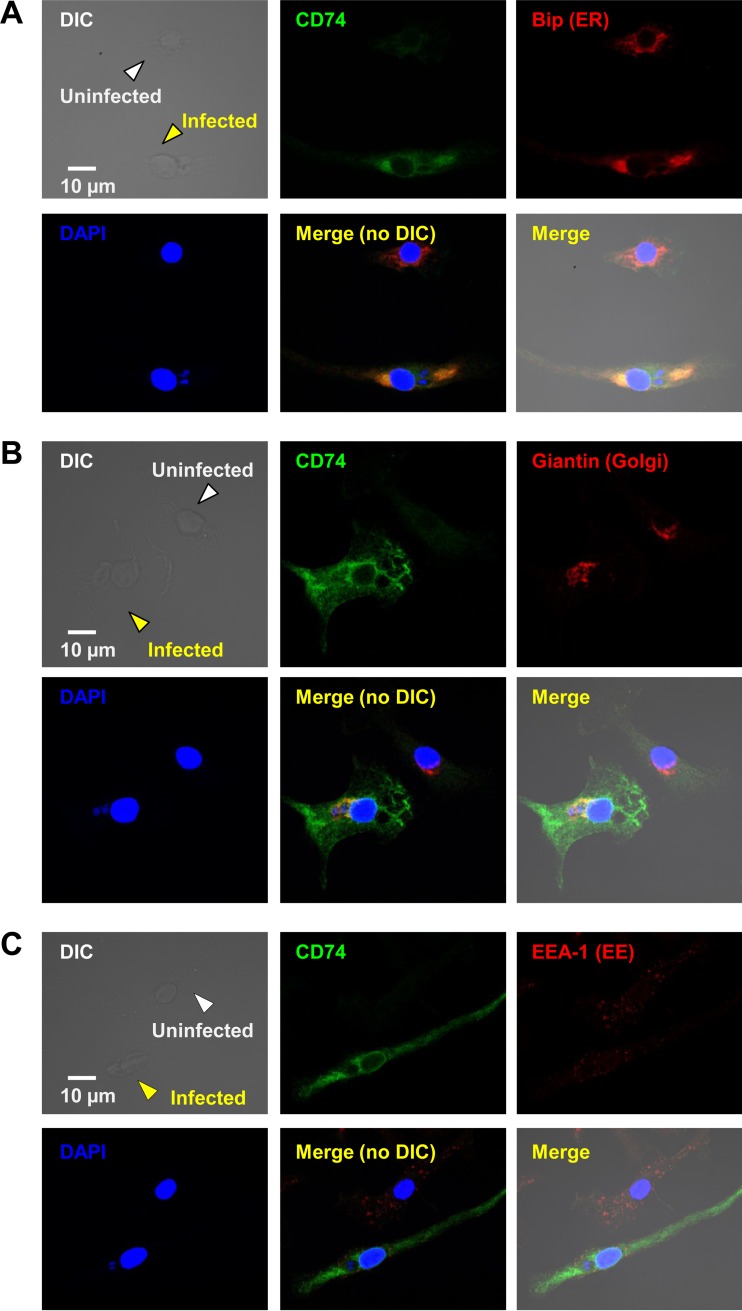
FIG 3.
CD74 accumulates mostly in the ER, but also in the Golgi apparatus and EE, in unstimulated, infected BMMϕ. Colocalization experiments for CD74 (green) were carried out with different markers for the ER (Bip) (A), the Golgi apparatus (Giantin) (B), and early endosomes (EEA-1) (C) (all red) in T. gondii-infected BMMϕ cultures (MOI = 2:1) left unstimulated. Z-stacks were acquired by confocal microscopy, followed by image processing, merging, and statistical calculations. Uninfected (white arrowheads) and infected (yellow arrowheads) cells are shown within the same fields. (A) Through statistical analyses, a colocalization coefficient (Rcoloc, where 1 is total colocalization and 0 no colocalization) of 0.73 and a threshold split Mander's coefficient (tM, where the total pixel intensity was normalized to avoid issues with absolute intensities) of 0.74 were obtained, suggesting significant colocalization of CD74 in the ER. (B and C) CD74 molecules were also found in the Golgi apparatus (Rcoloc = 0.41; tM = 0.37) (B) and EE (Rcoloc = 0.32; tM = 0.47) (C) to a much lesser extent. These fields are representative of entire cultures and of the results of three independent experiments.