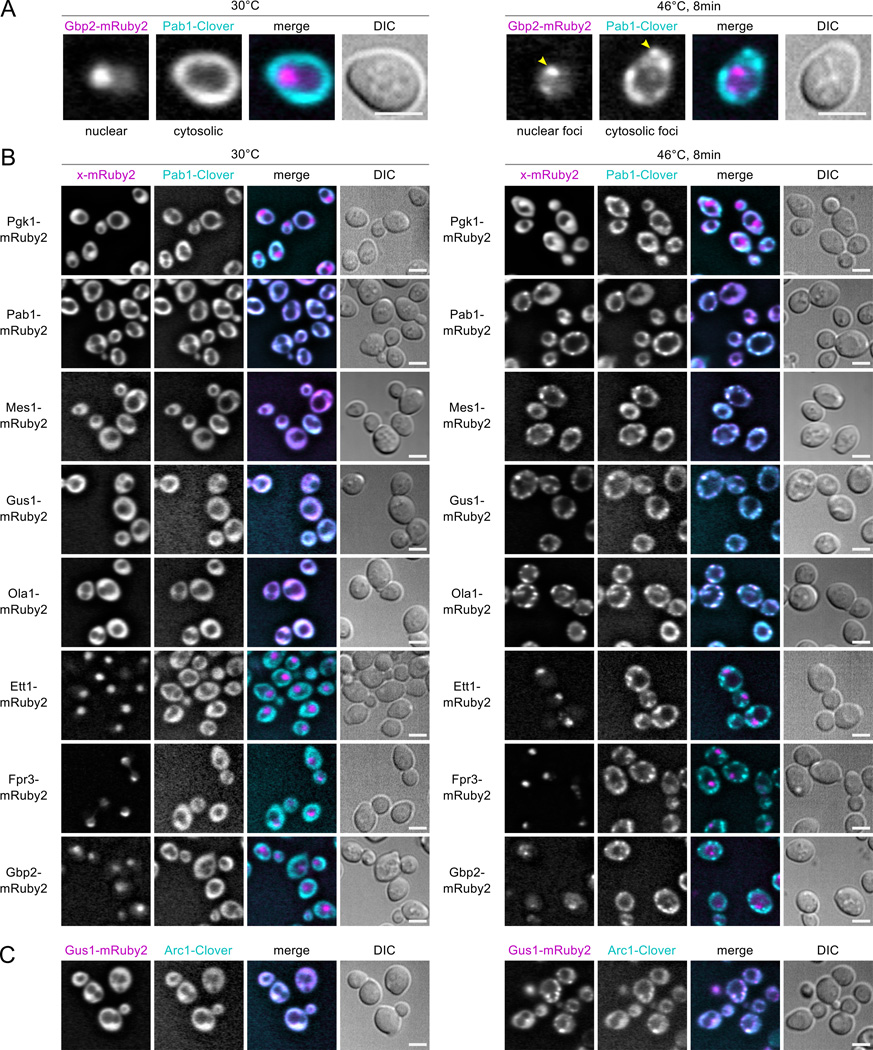
Figure 2.
Live-cell microscopy identifies heat-aggregating proteins forming cytosolic or nuclear granules. Diploid strains containing the HSG component Pab1 tagged with the green fluorescent protein (FP) Clover (cyan in merged images) and test proteins tagged with the red FP mRuby2 (magenta in merge) were imaged at 30°C and after 8 minutes’ heat shock at 46°C. Scale bar is 5 µm. A, Heat-induced nuclear and cytosolic aggregation of Gbp2- mRuby2 and Pab1-Clover, respectively. B, Non-aggregating Pgk1-mRuby2 remains diffuse during heat shock, while Pab1-Clover forms HSGs. Pab1-Clover and Pab1-mRuby2 form colocalized foci during heat shock. Fusions of MS-identified heat-aggregating proteins form foci that colocalize with Pab1 during heat shock (Mes1, Gus1, Ola1), or form subnuclear foci (Ett1, Fpr3, Gbp2). C, The aminoacylation cofactor in the multisynthetase complex, Arc1, forms heat-induced foci colocalized with Gus1.