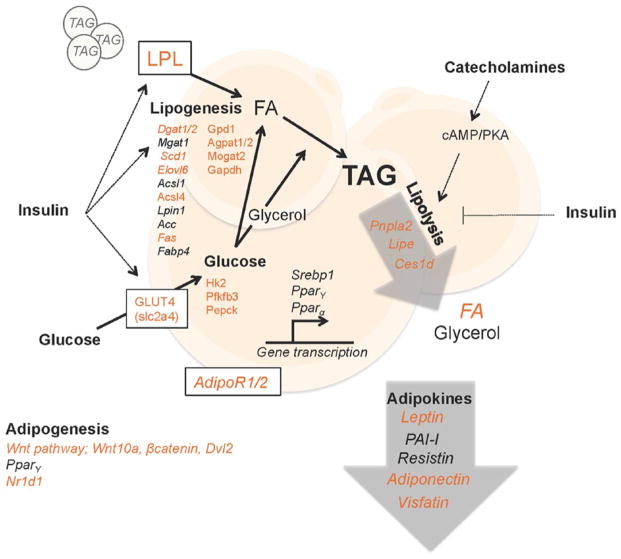
Figure 2.
The circadian clock regulates lipid metabolism in white adipose tissue. Adipocytes are cells that specialize in storing triacylglycerols (TAGs). TAGs are hydrolyzed in a process called lipolysis to produce soluble energy in the form of glycerol and fatty acids (FAs) when other tissues demand energy. Lipolysis is stimulated by catecholamines, which are mainly produced in the adrenal medulla. TAGs from the circulation constitute the majority of the stored lipids in adipocytes. TAGs are produced by esterification of FAs that are imported from the circulation, derived from circulating lipids that are hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase (LPL), or are produced from other substrates, such as glucose, in a process called de novo lipogenesis. Insulin acts on adipocyte metabolism in several ways, as indicated in the figure. In addition, adipose tissue is an endocrine organ, secreting essential endocrine factors called adipokines. The circadian clock coordinates lipid energy metabolism, partly through regulating the expression of enzymes, transporters, and adipokines. Genes and adipokines marked in italics are reported to display diurnal oscillation in expression. Those that are shown in orange font are direct targets of BMAL1/CLOCK and/or found altered in mice with a disrupted intrinsic clock. Lpl, lipoprotein lipase; Dgat1/2, diglyceride acyltransferase 1/2; Mgat1, monoglyceride acyltransferase 1; Scd1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1; Elovl6, elongation of very long-chain fatty acids protein 6; Acsl1/4, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1/4; Lpin1, phosphatidate phosphatase LPIN1; Ac1/2c, acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1/2; Fas, fatty acid synthase; Fabp4, fatty acid binding protein 4; Gpd1, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1; Agpat1/2, 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase 4; Mogat2, monoacylglycerol acyltransferase 2; Gapdh, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Hk2, hexokinase 2; Pfkfb3, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphospatase 3; Pepck, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; Srebp1, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; Ppar α/γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α/γ; AdipoR1/2, adiponectin receptor 1/2; Pnpla2 (Atgl), patatin-like phospholipase domain containing/adipose triglyceride lipase; Lipe (Hsl), hormone-sensitive lipase; Ces1d (Tgh), carboxylesterase 1D/triacylglycerol hydrolase; FA, fatty acid; Wnt10a, wingless-type MMTB integration site family member 10a; Dvl2, disheveled segment polarity protein 2; Nr1d1 (RevErbα), nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group D member 1; slc2a4 (GLUT4), solute carrier family 2/glucose transporter type 4.