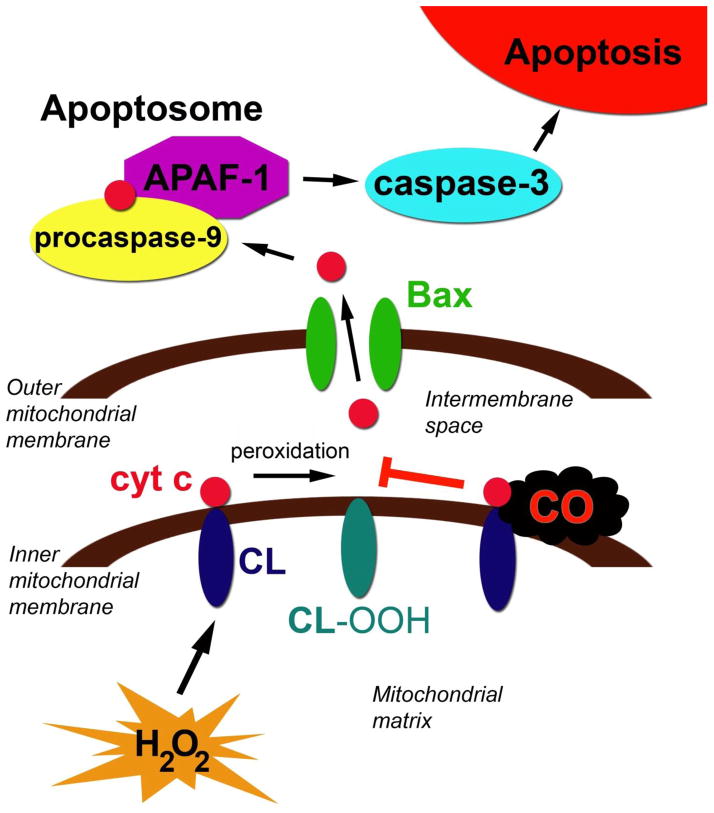
Figure 3. Mechanism of carbon monoxide (CO)-mediated inhibition of developmental apoptosis.
The mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis is depicted. Cytochrome c (cyt c), can bind to cardiolipin (CL) on the inner mitochondrial membrane via hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. Cyt c has peroxidase activity and, in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), peroxidizes CL to hydroperoxycardiolipin (CL-OOH). This mobilizes cyt c from the inner mitochondrial membrane and allows cyt c to be released following permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane by Bax. Subsequently, cyt c forms the apoptosome along with procaspase-9 and APAF-1. Caspase-9 then becomes activated and, in turn, activates caspase-3, resulting in apoptosis. CO readily diffuses across the outer mitochondrial membrane and binds to the cyt c-CL complex. CO inhibits the peroxidase activity of cyt c, preventing CL peroxidation, cyt c mobilization, cyt c release, and subsequent caspase activation.