Fig. 6.
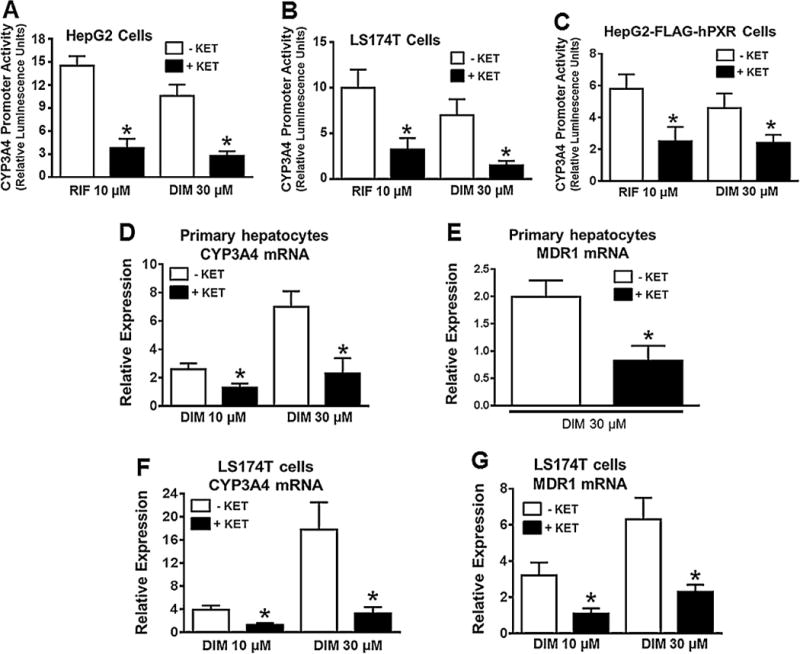
Pharmacologic inhibition of hPXR activity attenuates DIM-induced hPXR target gene expression in human primary hepatocytes, HepG2 and LS174 T cells. CYP3A4 prompter activity was determined in HepG2 (A) and LS174 T (B) cells after transiently co-transfecting the cells with pGL3-CYP3A4-luc reporter and pcDNA3-hPXR plasmids for 24 h, followed by treatment with DMSO, RIF or DIM in the presence and absence of PXR antagonist ketoconazole (KET) at 25 μM, as indicated for another 24 h. Similarly, CYP3A4 promoter activity was determined in HepG2-FLAG-hPXR cells (C) after transiently co-transfecting the cells with pGL3-CYP3A4-luc and CMV-Renilla. The induction of CYP3A4 promoter activity by the treatment was normalized as fold increase over the DMSO control. Data represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Statistical significance (*, p < 0.05) was determined using Students t test by comparing RIF or DIM alone with the combined RIF + KET or DIM + KET. mRNA expression of CYP3A4 and MDR1 was determined by quantitative RT-PCR in primary human hepatocytes (HU1488) (D & E) and LS174 T cells (F & G) after treatment with DMSO, RIF or DIM in the presence and absence of 25 μM KET, as indicated for 48 h. Results are presented as fold increase over the DMSO control. In all graphs, data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Statistical significance (*, p < 0.05) was determined using Students t test by comparing RIF or DIM alone with the combined RIF + KET or DIM + KET.
