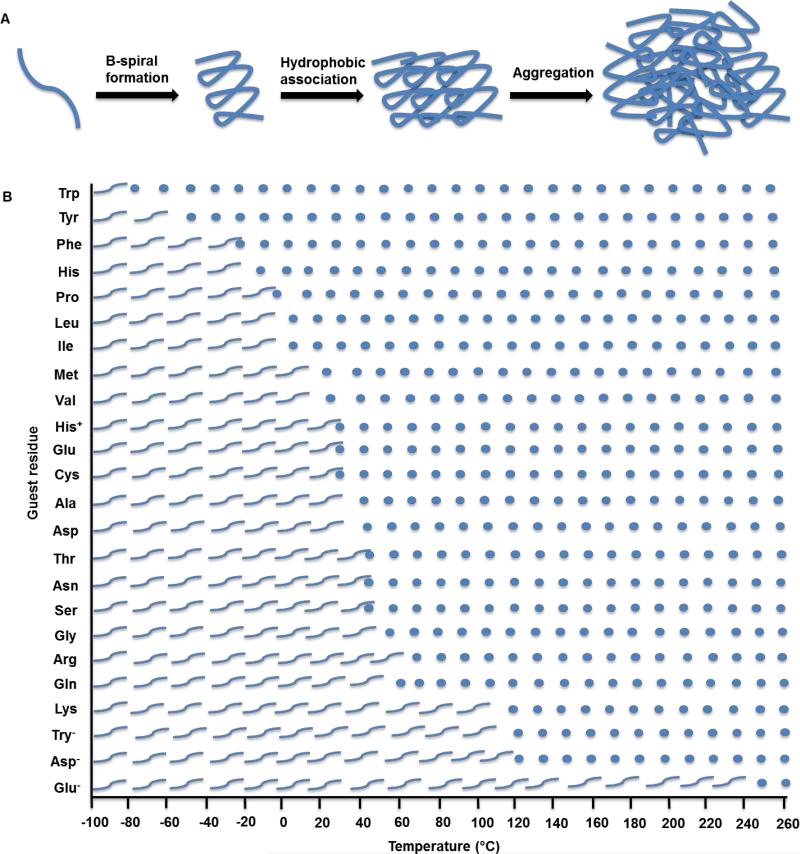
Figure 3.
A) The mechanism of ELP transition from a soluble state to a coacervated state at the transition temperature. ELP monomers form β-spirals which are stabilized by hydrophobic interactions. The polypeptide chains then associate into larger aggregates. B) Effect of the guest residue X on the coacervation temperature of [VPGXG]n ELPs. Wavy lines represent ELPs in soluble form below their inverse transition temperatures, while circles represent coacervated ELPs.