Fig. 1.
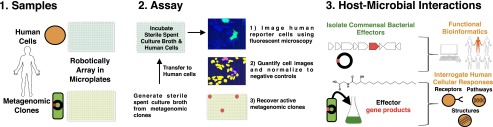
Overview of metagenomic methods. Step 1: The human reporter cell line and individual metagenomic bacterial clones are robotically arrayed in separate 384-well microplates. Step 2: Mature bacterial cultures are filter sterilized, and sterile spent culture broth is then transferred to plates containing the human reporter cell line. Human reporter cells that have been exposed to spent culture broth are imaged by fluorescent microscopy to identify metagenomic clones that activate the reporter. Step 3: Once an active metagenomic clone is confirmed, the specific effector genes are identified through sequencing and transposon mutagenesis, and the effector molecules (proteins or small molecules) are characterized from large-scale cultures of the active metagenomic clone.
