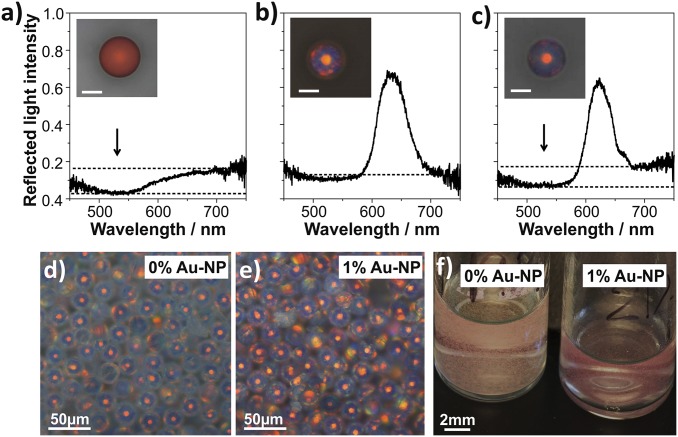
Fig. 3.
Color purification by incorporation of spectrally selective absorbers. (A) Reflection spectra of a disordered photonic ball (binary mixture of colloids with d = 200 nm and 250 nm) with 12-nm Au nanoparticles (NPs). The absorption of the Au NPs lowers the reflection of light in the blue/green part of the spectrum (arrow), giving the ball a dull, red appearance (A, Inset). (B) An ordered photonic ball (dcolloids = 250 nm) shows a Bragg reflection peak at 620 nm, leading to a bright, red color (Inset). (C) An ordered photonic ball with gold nanoparticles shows lowered reflection at the blue/green part of the spectrum without affecting the Bragg reflection peak. (D–F) Control of scattering properties by addition of Au NPs in ensembles of photonic balls. Microscopic images (D and E, taken with identical exposure times) and macroscopic images (F) reveal an increased contrast.