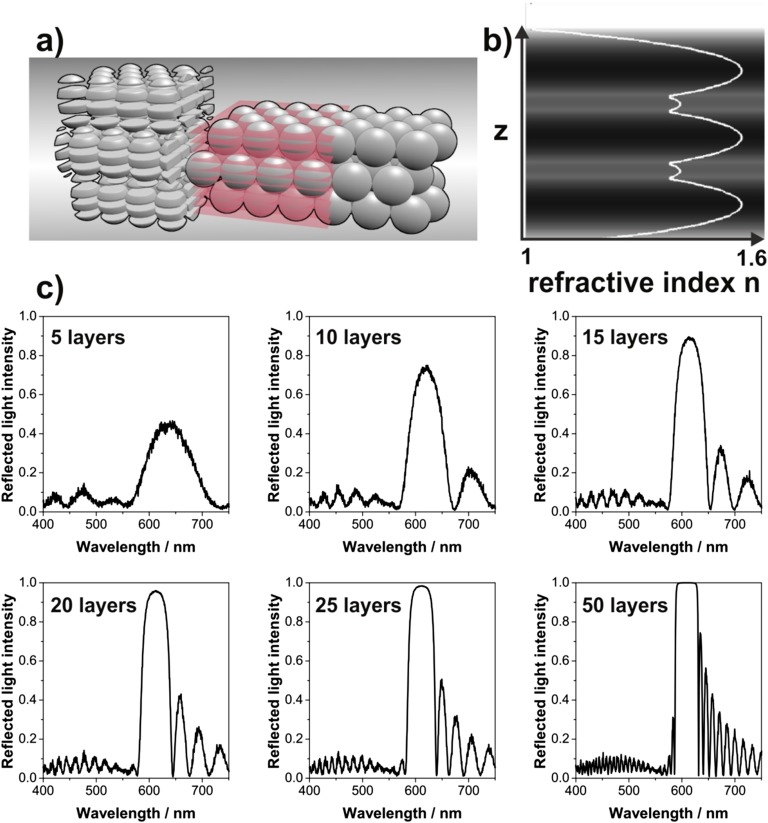
Fig. S3.
Explanation of one-dimensional (1D) transfer matrix calculation of reflectance spectra for photonic balls. The multilayer structure of the ball is simulated as a noncurved thin film; the disorder in the ball’s interior is approximated by a random refractive index material underneath the multilayer structure. (A) Schematic showing the division of the film into discretized layers for averaging to generate an analog 1D multilayer structure. (B) Color plot with line plot overlay showing the refractive index variation along the normal direction of a three-layer polystyrene opal film (darker colors indicate higher refractive indexes). The refractive index was calculated by laterally averaging the permittivity of the opal for each slice. Additional numbers of layers are easily included by repeating the refractive index profile as desired. (C) Calculated reflectance spectra, exemplarily shown for opal films with a colloid size of 250 nm and different numbers of layers. The additional peaks around the main Bragg reflection peak are caused by thin-film interference effects.