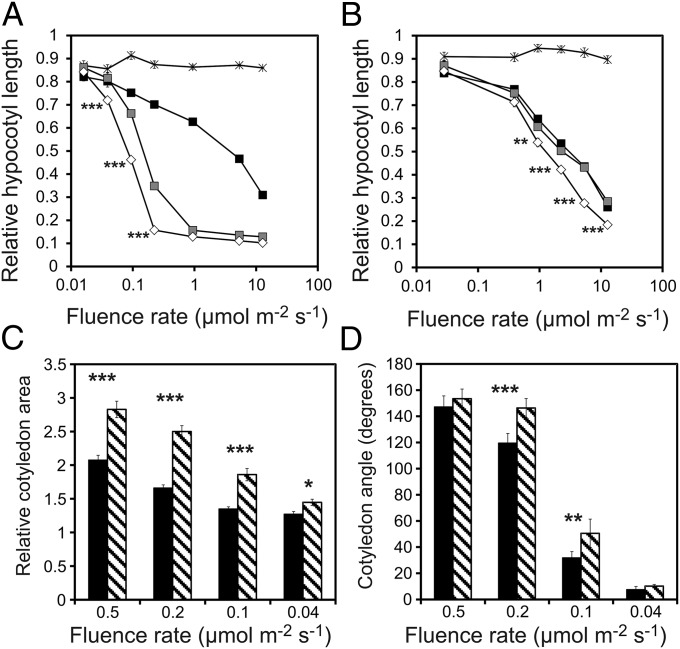
Fig. 2.
Seedlings expressing the mutant phyBLys996Arg-YFP are hypersensitive to RL. Relative fluence rate-dependent inhibition of hypocotyl elongation of wild-type Col-0 (black square), phyB-9 (star symbol), and transgenic phyB-9 plants expressing phyB-GFP (gray square) or phyBLys996Arg-YFP (white diamond) under the control of the constitutively active (A) viral 35S promoter or (B) the Arabidopsis LIP1 promoter is shown. Seedlings were grown in darkness or at the indicated fluence rates of RL for 4 d. Hypocotyl lengths of irradiated seedlings were measured, and the average value of 25–30 seedlings was calculated and normalized to the hypocotyl length of D-grown plants. (C) Transgenic phyB-9 seedlings expressing 35S:PHYB-GFP (black columns) or 35S:PHYBLys996Arg-YFP (striped columns) were grown at the indicated fluence rates of RL for 4 d. Cotyledon areas of irradiated seedlings were measured, and the average value was normalized to the cotyledon area of D-grown plants. (D) Cotyledon angle of D- or RL-grown seedlings analyzed in Fig. 3C was measured. All experiments shown in Fig. 2 were repeated three times. Error bars indicate SE. Asterisks show statistically significant differences between phyB-GFP or phyBLys996Arg-YFP expressor plants as determined by Student’s t test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).