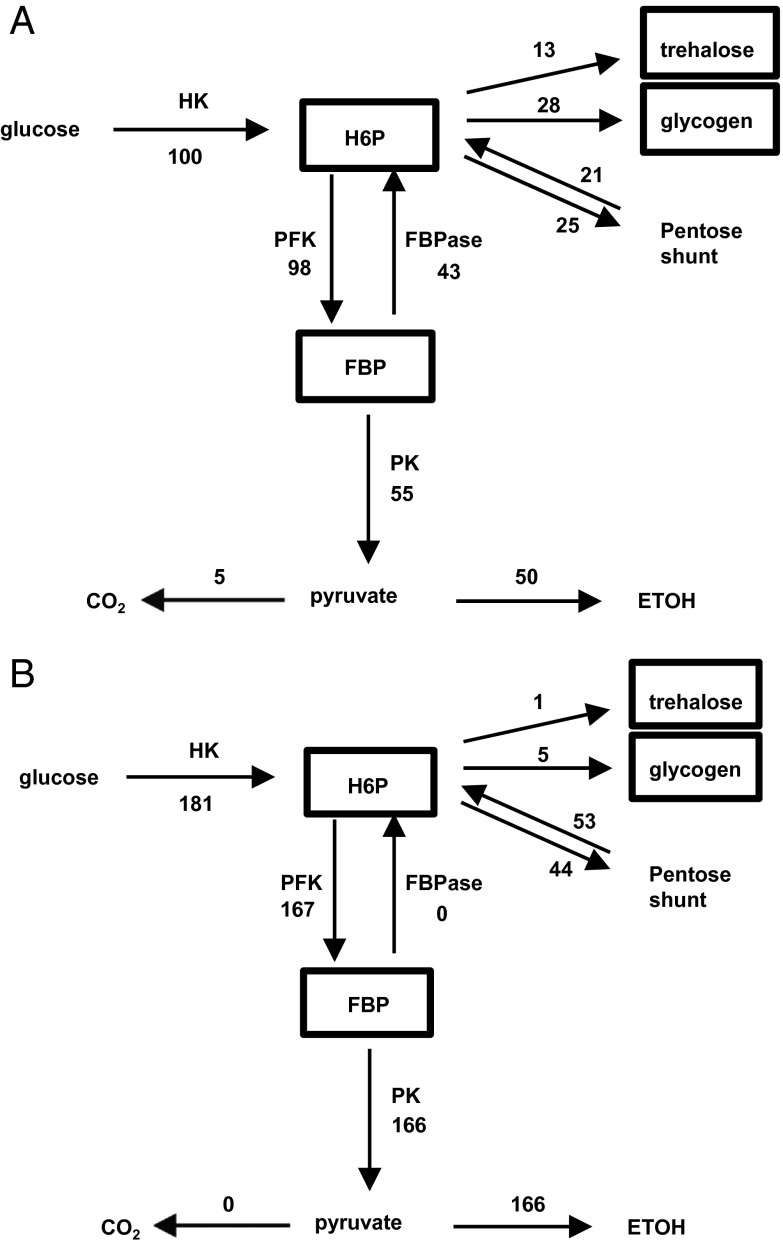
Fig. 1.
Metabolic fluxes of glucose consumption in yeast after exposure to high glucose levels under aerobic (A) and anaerobic (B) conditions. The fluxes are normalized to glucose uptake in the aerobic case, which is set to 100 (A). Respiratory-competent yeast grown on acetate were exposed to 50 mM glucose in a nongrowth medium. FBP, fructose 1, 6, bis phosphate; FBPase, fructose biphosphatase; HK, hexokinase; HMP, sum of hexose monophosphates glucose 6 phosphate, fructose 1 phosphate, and trehalose 6 phosphate; PFK, phosphofructokinase; PK, pyruvate kinase. Of particular note in the aerobic case is the high amount of glucose uptake (100) relative to the rate of oxidation in the TCA cycle to CO2 (5), with a large fraction converted to ETOH.