Fig. 1.
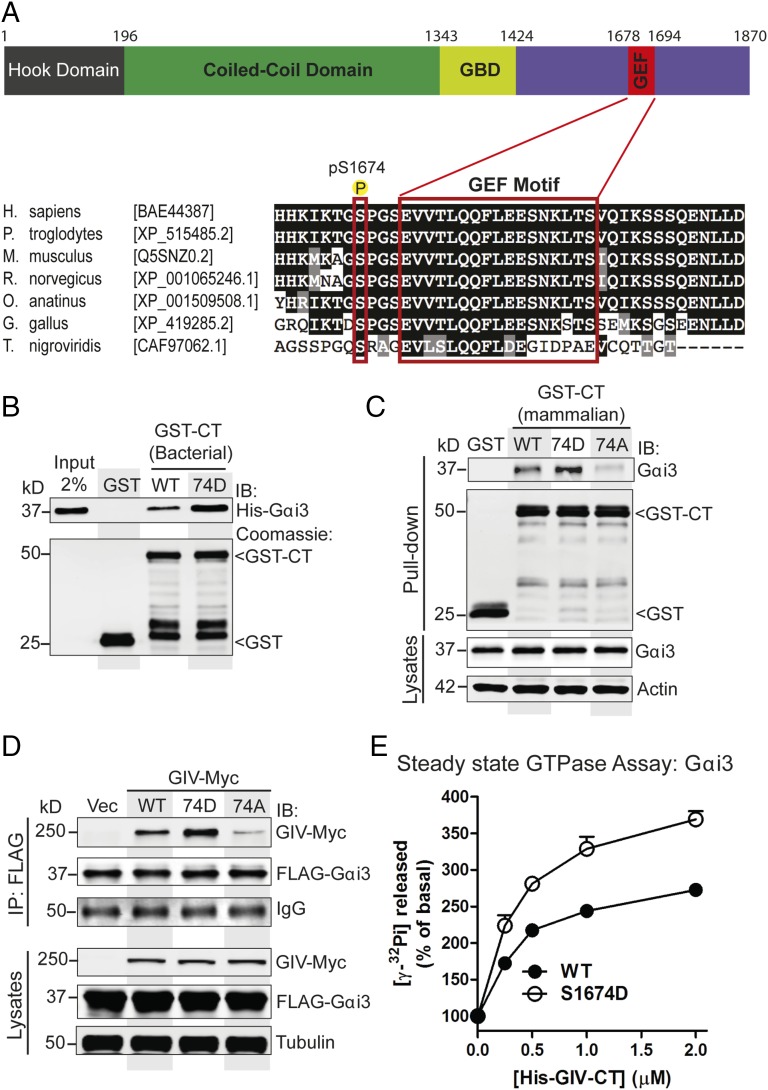
Phosphomimetic S1674D (74D) mutation enhances GIV's ability to bind and activate Gαi3, whereas the nonphosphorylatable S1674A (74A) mutation abolishes binding. (A) Schematic of the domain architecture of GIV and sequence alignment of its C-terminal GEF motif. (Top) Various domains of GIV are shown including the N-terminal microtubule-binding hook domain, coiled-coil domain, Gα-binding domain (GBD), and the C-terminal domain containing the GEF motif. The residue numbers marking the boundaries of each domain are shown. (Bottom) The sequence encompassing the GEF motif (in red rectangle) and surrounding residues was aligned among various species (accession numbers are shown in brackets) using ClustalW. Conserved residues are shaded in black and similar residues in gray. The most heavily phosphorylated residue in the C terminus as determined by mass spectrometry (S1674 in human GIV) is boxed in red. (B) Equimolar amounts of purified His-Gαi3 were incubated with purified GST or GST-GIV-CT proteins immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads. Bound His-Gαi3 was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-His antibody. (C) Lysates of Cos7 cells expressing WT or mutant (74D or 74A) GST-GIV-CT were incubated with glutathione-Sepharose beads. Bound proteins (Upper) were analyzed by immunoblotting for endogenous Gαi3. Equal loading was confirmed by immunoblotting the pull-downs for GST and GST-GIV CT and the lysates for Gαi3 and actin. (D) Immunoprecipitation (IP) was carried out with anti-FLAG antibody on equal aliquots of lysates of Cos7 cells coexpressing FLAG-Gαi3 and full-length Myc-tagged GIV-WT, 74D, or 74A followed by incubation with protein-G Sepharose beads. Bound immune complexes (IP) were analyzed for FLAG (Gαi3) and Myc (GIV) by immunoblotting, and equal loading of lysates was confirmed by immunoblotting for tubulin. (E) The steady-state GTPase activity of His-Gαi3 (50 nM) was determined in the presence of increasing amounts (0–2 μM) of purified His-GIV-CT WT (solid circles) and 74D (open circles). Gαi3 activation is expressed as percent of the steady-state GTPase activity of Gαi3 alone. Results are shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Activation of Gαi3 by GIV-CT is enhanced in the case of the 74D mutant compared with its WT counterpart.