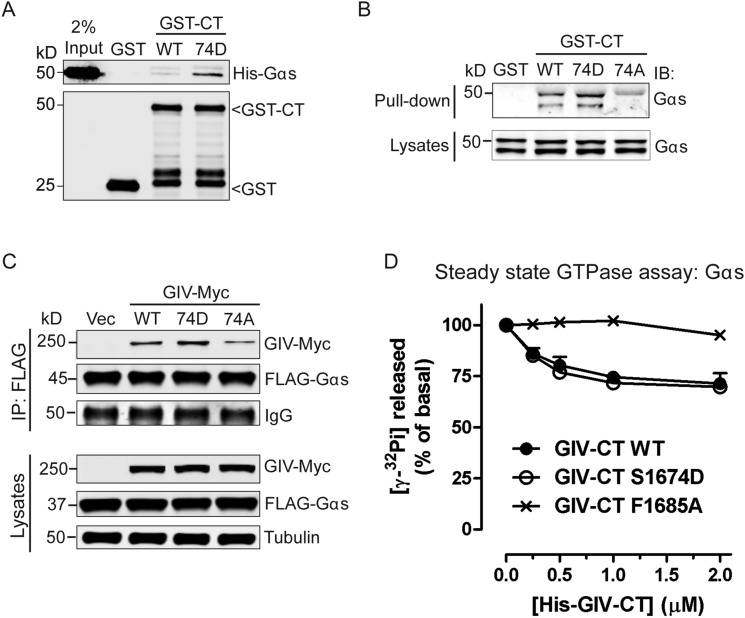
Fig. S1.
Phosphomodification of S1674 enhances GIV–Gαs interaction. (A) Phosphomimetic mutation at S1674 (74D) in GIV enhances its ability to bind Gαs in vitro. Equimolar amounts of purified His-tagged Gαs were incubated with bacterially expressed and purified GST, WT, or 74D GST-GIV-CT (1660–1870) immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. Input represents 2% of the total His-tagged Gαs used in the binding reactions. n = 3. (B) Nonphosphorylatable GIV-74A mutant (74A) shows impaired binding to Gαs in cells. Cos7 cells were transiently transfected with WT, 74D, or 74A GST-GIV-CT, and clarified cell lysates were incubated with glutathione-Sepharose beads. Bound proteins and lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for endogenous Gαs. n = 3. (C) Gαs preferentially coimmunoprecipitates with the phosphomimetic but not the nonphosphorylatable form of full-length GIV. Immunoprecipitation was carried out with anti-FLAG antibody on equal aliquots of Cos7 lysates coexpressing FLAG-Gαs and full-length Myc-tagged GIV-WT, 74D, or 74A followed by incubation with protein G-Sepharose beads. Bound immune complexes were analyzed for FLAG and Myc by immunoblotting, and equal loading was confirmed by immunoblotting for tubulin (lysates). n = 3. (D) His-GIV-CT WT and 74D, but not His-GIV-CT F1685A, decrease the steady-state GTPase activity of His-Gαs in a dose-dependent manner. The steady-state GTPase activity of purified His-Gαs (50 nM) was determined in the presence of the indicated amounts of purified His-GIV-CT WT (closed circles) or mutants (74D, open circles; F1685A, cross symbol) by quantification of the amount of [γ-32P]GTP (0.5 μm, ∼50 cpm/fmol) hydrolyzed in 15 min. Data are expressed as percent of GTP hydrolyzed by the G protein alone (0 μM). Results are shown as mean ± SD of two independent experiments.