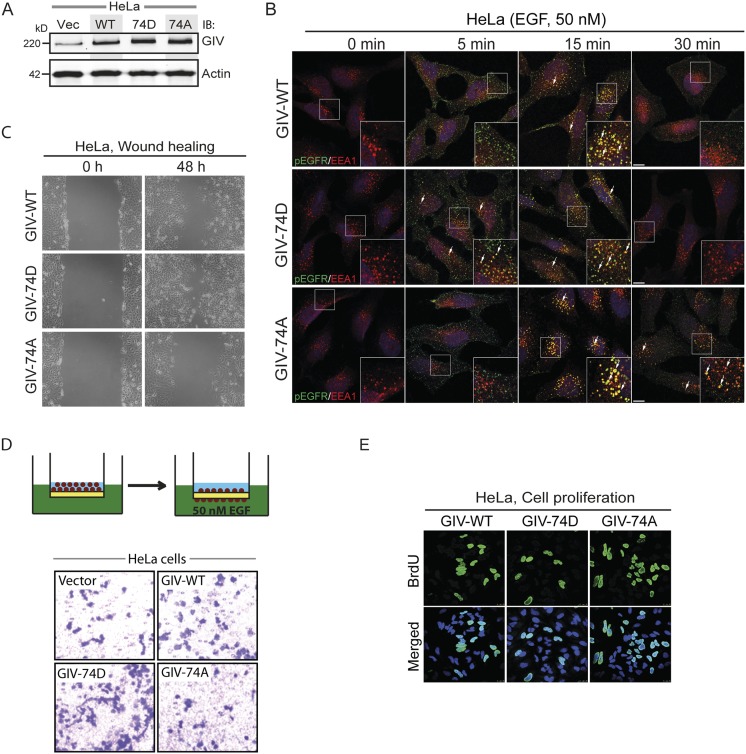
Fig. S2.
Phosphorylation of S1674 affects EGFR trafficking to and signaling from early endosomes as well as the balance of migration–proliferation dichotomy in HeLa cells. (A) GIV expression in HeLa stable cell lines expressing WT, 74D, and 74A constructs. Equal aliquots of whole-cell lysates of parental (vector alone; Vec), GIV-WT, GIV-74D, and GIV-74A HeLa cell lines were analyzed for GIV and actin by immunoblotting (IB). (B) The nonphosphorylatable GIV mutant prolongs EGFR activation at EEA1 endosomes. HeLa cells stably expressing GIV-WT, 74D, and 74A were treated with 50 nM EGF for the indicated time points, fixed, and stained for activated (phosphorylated) pY1068-EGFR (green) and EEA1 (red). Arrows pointing to yellow pixels in the images denote colocalization of pEGFR and EEA1. (Insets) Enlargement (3×) of boxed regions. (Scale bars, 10 μm.) n = 3. (C) Phospho-status of S1674 on GIV influences cell migration. HeLa cells stably expressing GIV-WT, GIV-74D, and GIV-74A were subjected to scratch wounding and examined immediately after wounding (0 h) and 48 h later (n = 3). The GIV-74D cells showed enhanced migration in scratch-wound assays compared with cells expressing GIV-WT, whereas the GIV-74A showed decreased cell migration. (D) GIV-74D enhances cell migration in response to EGF. Chemotaxis of HeLa cells toward EGF supplemented serum-free medium was evaluated using a Transwell migration assay (schematic shown on Top). Cells were allowed to migrate for 6 h and were fixed and stained with Toluidine Blue. Representative images are shown for vector, WT, 74D, and 74A cells. (E) GIV-74A mutation enhances cell proliferation. HeLa cells stably expressing GIV-WT, GIV-74D, and GIV-74A were grown in low serum [2% (vol/vol) FBS] overnight, incubated in BrdU for 30 min, fixed [3% (wt/vol) paraformaldehyde], stained for BrdU, and analyzed by confocal microscopy (n = 3). Representative images are shown for WT, 74D, and 74A cells. Green, BrDU; blue, DAPI.