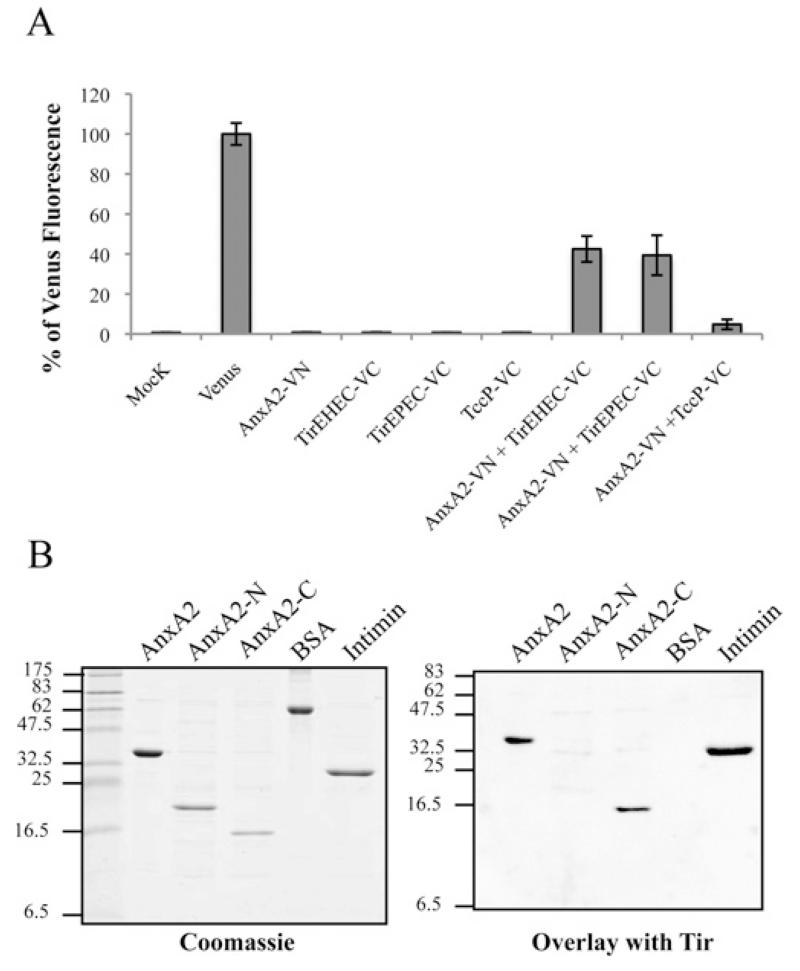
Figure 4. AnxA2 binds Tir-EPEC and Tir-EHEC through its C-terminal domain.
(A) Measured BiFC signal intensities determined by FACS in COS-7 cells. Results are means ± S.D. for three independent experiments (10000 cells/experiment) expressed as percentages of the signal intensity obtained with an equivalent amount (500 ng) of the pVenus plasmid. (B) Identification of Tir-binding sites on AnxA2. Protein overlay assay showing binding of Tir-EHEC to AnxA2. Purified full-length human AnxA2, AnxA2-N (amino acids 1–190), AnxA2-C (amino acids 191–339), BSA and intimin (Int280γ ) proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue (left-hand panel) or immobilized on to PVDF membranes and incubated with purified His6–Tir-EHEC (right-hand panel). Bound Tir-EHEC was detected by immunostaining with rabbit polyclonal anti-Tir antibodies followed by alkaline phosphatase-linked anti-(rabbit IgG) antibody, showing specific interaction of Tir with the intact C-terminal AnxA2 region. Molecular masses are indicated in kDa.