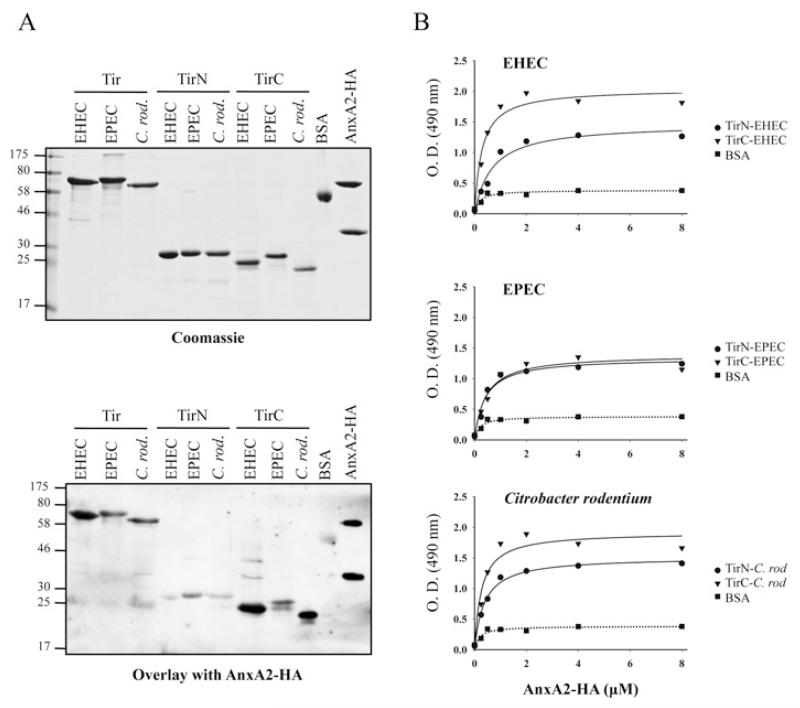
Figure 5. TirN and TirC from EHEC, EPEC and C. rodentium bind AnxA2 with different affinities.
(A) Protein overlay assay showing binding of AnxA2 to Tir-EHEC, Tir-EPEC and Tir-C. rodentium (C. rod.) derivatives. Purified full-length Tir, TirN and TirC from EHEC, EPEC and C. rodentium were separated by SDS/PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue (upper panel) or immobilized on to PVDF membranes and incubated with purified AnxA2–HA (lower panel). Bound AnxA2 was detected with horseradish-peroxidase-conjugated anti-HA antibodies. Molecular masses are indicated in kDa. (B) ELISA quantification of binding of AnxA2 to EHEC, EPEC and C. rodentium TirN and TirC fragments. A range of concentrations of purified AnxA2–HA were added to microtitre plate wells coated with EHEC (top panel), EPEC (middle panel) or C. rodentium (C. rod) (bottom panel) purified TirN, TirC or BSA proteins. Binding was detected with horseradish-peroxidase-conjugated anti-HA antibodies. O.D. = absorbance.