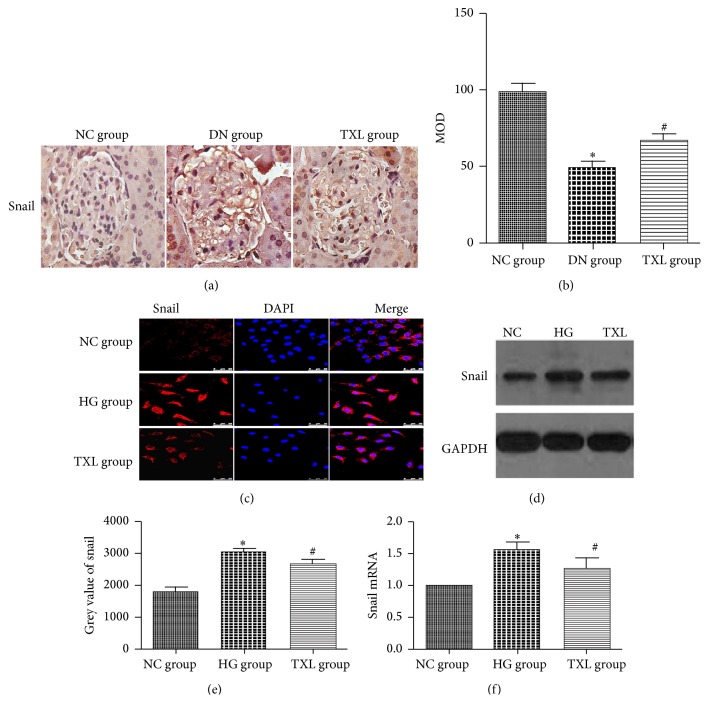
Figure 4.
Effect of TXL on snail expression in diabetic rats and high glucose cultured podocyte. (a) Representative immunohistochemical photograph for snail in vivo. Immunohistochemical results showed that nephrin protein expression was significantly increased and translocated from cytoplasm to nucleus in DN group. TXL decreased snail protein expression and inhibited the translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus in diabetic rats. (b) Comparison of mean optical density (MOD) of snail protein in rats. The result showed that snail protein was statistically significantly decreased in DN group compared with NC group (P < 0.05). Snail protein expression was significantly increased in TXL group compared with DN group (P < 0.05). (c) Representative photograph of snail staining (red) and cell nucleus (DAPI blue). High glucose increased snail expression and promoted snail translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus, and TXL inhibited snail expression and nuclear translocation. (d) Representative band of snail protein by western blot in cultured podocyte. (e) Comparison of the grey value of snail protein in cultured podocyte (n = 3). The result showed that snail protein was statistically significantly increased in HG group compared with NC group (P < 0.05). Snail protein expression was significantly decreased in TXL group compared with HG group (P < 0.05). (f) Comparison of mRNA level of snail by RT-PCR in cultured podocyte (n = 3). The result showed that snail mRNA was statistically significantly increased in HG group compared with NC group (P < 0.05). Snail mRNA expression was significantly decreased in TXL group compared with HG group (P < 0.05). ∗ P < 0.05 versus NG. # P < 0.05 versus HG.