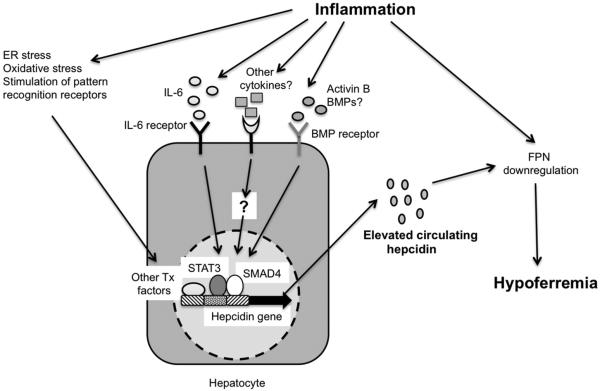
Figure 2. The major factors contributing to hypoferremia during inflammation.
Inflammatory stimuli such as IL-6 (Interleukin-6), other cytokines, activin B, BMPs (Bone morphogenetic proteins), endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and oxidative stress, and pattern recognition receptor ligands activate STAT3 (Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3), SMAD4 (Small-mothers against decapentaplegic-4) and other transcription (Tx) factors to induce increased expression of hepcidin, leading to downregulation of FPN (Ferroportin) and consequent hypoferremia. Inflammatory mediators may also act directly to cause decreased expression of FPN. For clarity, inflammation-associated factors that inhibit hepcidin expression have not been shown.