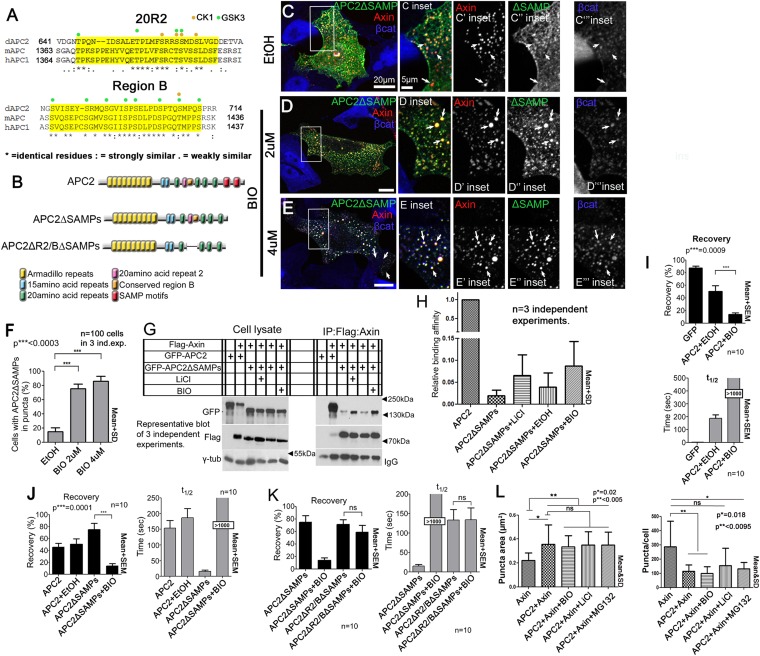
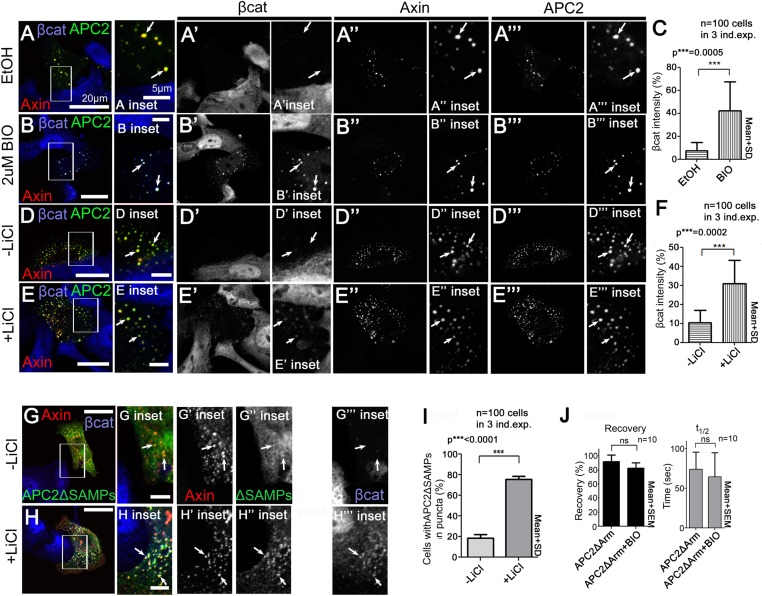
Figure 7. Axin:APC2 Arm rpts association is regulated by GSK3.
(A) R2 and B of Drosophila dAPC2, mouse mAPC1 and human hAPC1. Potential CK1(orange) and GSK3(green) phosphorylation sites. (B) APC2 mutants. (C–E) SW480 cells expressing GFP-APC2ΔSAMPs and Axin-RFP. Insets = boxes in C–E (C) Control (Ethanol treated (EtOH)). Deleting the SAMPs reduces APC2:Axin colocalization (arrows). (D) 2 μM BIO enhances APC2ΔSAMPs recruitment into Axin puncta. (E) Increasing BIO to 4 μm further boosts APC2ΔSAMPs recruitment into Axin puncta. (F) Quantification of (C–E). (G) CoIP of APC2∆SAMPs with Axin in SW480 cells ± LiCl or BIO. Full length APC2 is a control. Deleting the SAMPs drastically reduces coIP but GSK inhibition partially restores this. (H) Quantification of coIP in G, >2 replicates, normalized to Axin. (I) FRAP assay, SW480 cells transfected with Axin-RFP + GFP-APC2. GSK3 inhibition decreases APC2 dynamics. (J) GSK inhibition also slows APC2ΔSAMPs dynamics. (K) Deleting R2/B in APC2ΔSAMPs abolishes effect of GSK3 inhibition on dynamics. Student's t-test. (L) GSK3 inhibition with either BIO or LiCl does not further increase the size or decrease the number of APC plus Axin puncta, nor does treatment with the proteasome inhibitor MG132. Puncta area and puncta number, from confocal images.