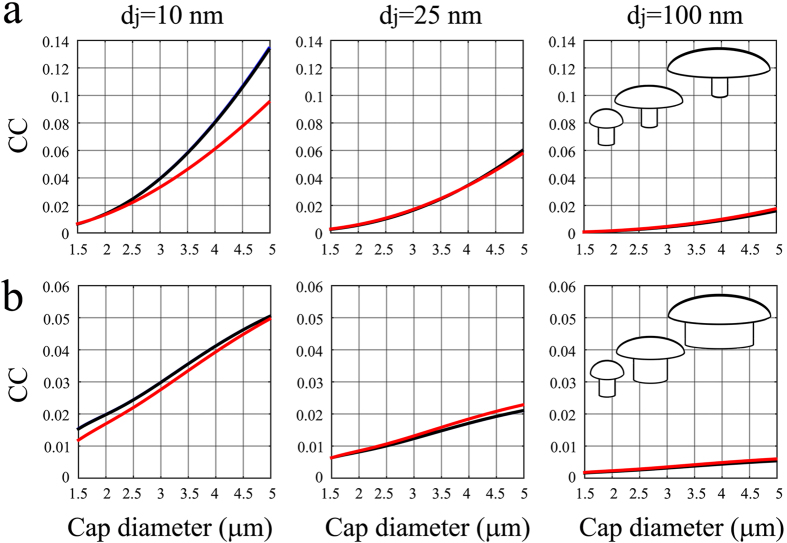
Figure 6. The electrical coupling coefficient between neurons and gold mushroom shaped microelectrodes (gMμEs) as a function of the mushroom cap diameters.
Two modes of size change were considered (Fig. 5b,c): in (a) Model A, the stalk diameter was kept constant while the cap diameter was increased; in (b) Model B, the diameter of the mushrooms cap and stalk increased, keeping the gMμE cap diameter 1 μm larger than the stalk. The simulations were conducted assuming a homogeneous membrane-gMμE cleft thickness (dj) of 10, 25 or 100 nm, for three impulse frequencies depicting membrane oscillations (10 Hz), synaptic potentials (100 Hz, both oscillations and synaptic potentials are depicted by a black curve) and action potentials (1 kHz, red) and for junctional membrane resistivity (Rjm) of 80 Ωcm2. All parameters related to the dimensional changes of the simulated gMμEs (Rjm, Cjm; Rs; Re, Ce) were integrated in the simulations using a specific membrane capacitance of 1 μF/cm2.