Figure 3.
Mutations in dcl1 and dcl4 Show a Synergistic Interaction.
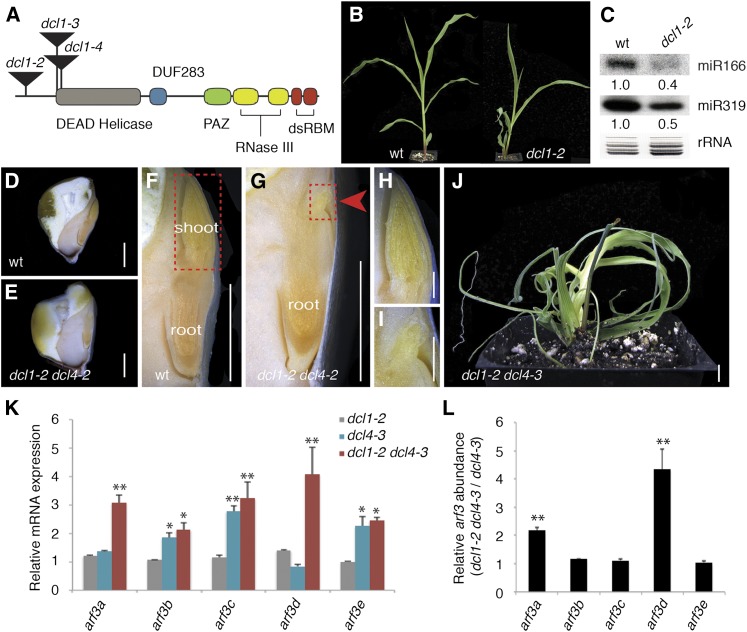
(A) Diagrammatic representation of DCL1 with conserved domains and positions of transposon insertions in the dcl1 alleles indicated.
(B) Compared with the wild type, dcl1-2 mutants develop upward curling leaves that are partially adaxialized.
(C) Small RNA gel blot showing miR166 and miR319 levels are reduced in dcl1-2 shoot apices.
(D) to (I) Relative to the wild type ([D], [F], and [H]), the embryonic shoot of dcl1-2 dcl4-2 mutants ([E], [G], and [I]) is dramatically reduced (arrow in [G]). Red boxes in (F) and (G) mark shoot regions enlarged in (H) and (I), respectively.
(J) dcl1-2 dcl4-3 seedlings similarly reveal a synergistic interaction and resemble mutants blocked at early steps in ta-siRNA biogenesis.
(K) and (L) The severity of the dcl1-2 dcl4-3 phenotype is marked by elevated expression of arf3a and arf3d specifically. arf3 transcript levels in dcl1-2, dcl4-3, and dcl1-2 dcl4-3 shoot apices (means ± se) normalized to the wild type (K) were calculated based on three independent biological replicates. arf3 expression values (means ± se) in dcl1-2 dcl4-3 normalized to dcl4-3 (L) show arf3a and arf3d transcript levels specifically are increased in dcl1-2 dcl4-3 (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01).
Bars in (D) to (J) = 5 mm.