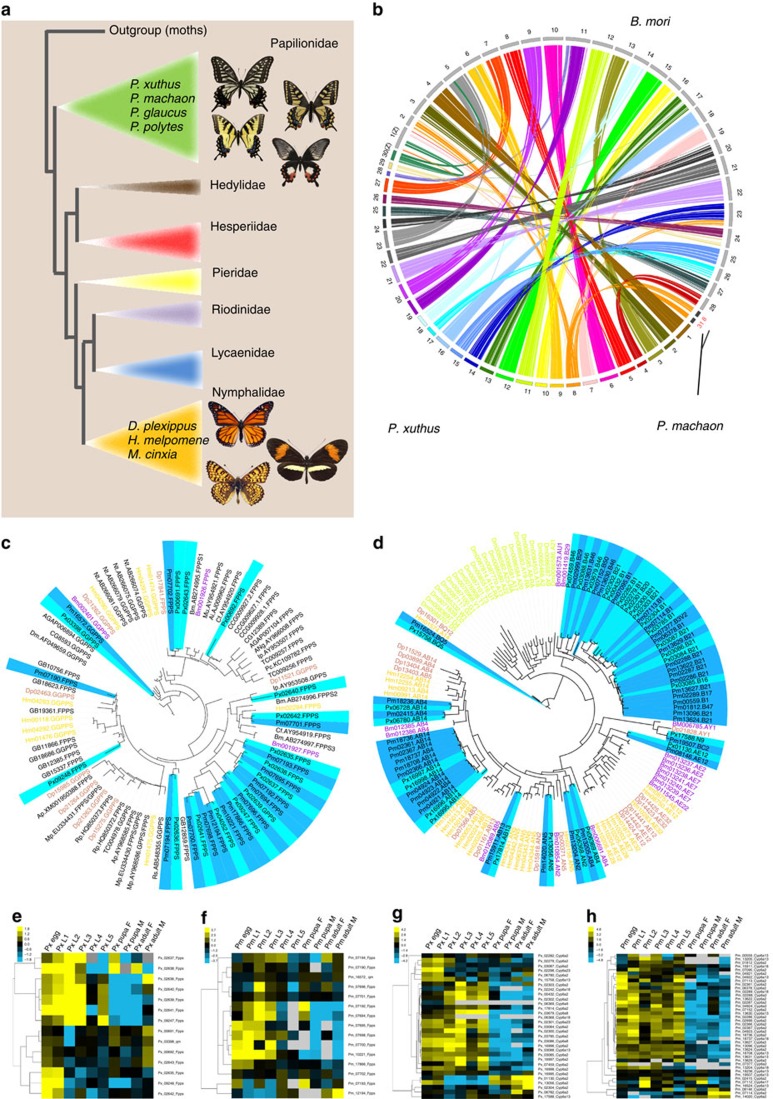
Figure 1. Butterfly comparative genomics.
(a) Phylogeny of butterfly families58 showing relationship of P. xuthus and P. machaon to D. plexippus, H. melpomene, M. cinxia, P. glaucus and P. polytes. (b) Chromosome mapping of P. xuthus (n=30) to B. mori (n=28). For P. machaon (n=31), we only plot chromosome 8 (chr8) and chr31, which were fused in P. xuthus. (c) Maximum-likelihood tree showing strong expansion of the scIPPS genes in the genomes of swallowtail butterflies. Included are all scIPPS genes identified in the genomes of ten holometabolous insects (P. xuthus, P. machaon, D. plexippus, H. melpomene, B. mori, P. xylostella, A. gambiae, D. melanogaster, T. castaneum and A. mellifera). The clades of P. xuthus and P. machaon are highlighted by light blue and deep blue, respectively. (d) Maximum-likelihood tree showing expansions of CYP6B genes in the genomes of P. xuthus and P. machaon, and of the CYP6AB genes in the genome of P. machaon, as compared with CYP6 genes of D. plexippus, H. melpomene, B. mori and D. melanogaster. In c,d, the clades of P. xuthus and P. machaon are highlighted by light blue and deep blue, respectively. (e,f) Expression profiles of FPPS and GGPPS genes at all development stage of P. xuthus (e) and P. machaon (f). (g,h) Expression profiles of CYP6 genes at all development stage of P. xuthus (g) and P. machaon (h). Expression measured in reads per kilobase of transcript per million reads mapped (RPKM).