Fig. 1.
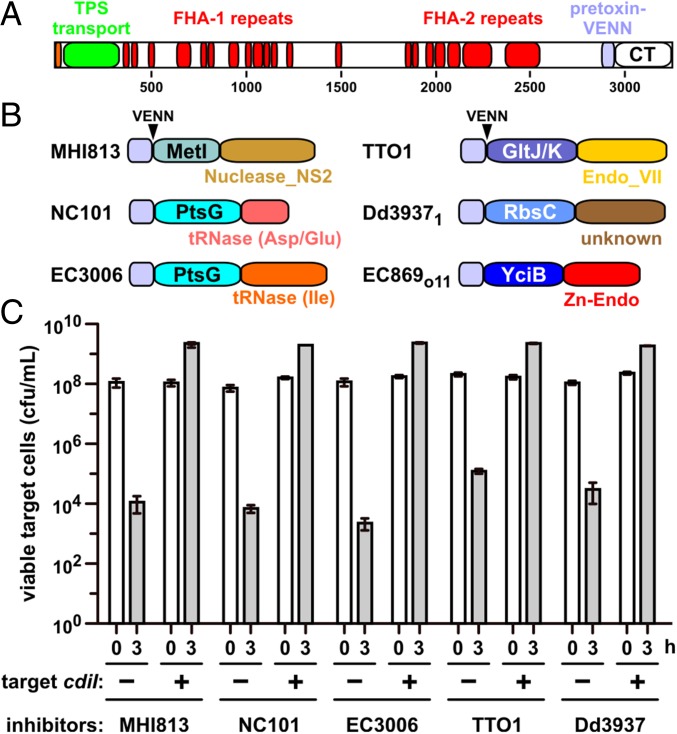
Activity of CdiA chimeras. (A) CdiA proteins contain an N-terminal TPS transport domain and two filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA)-peptide repeat regions. The pretoxin-VENN domain is adjacent to and demarcates the variable CdiA-CT region. (B) Predicted CdiA-CT domain structures. Toxins from E. coli MHI813 and Photorhabdus luminescens TTO1 carry predicted C-terminal Nuclease_NS2 (Pfam database ID: PF13930) and Endonuclease_VII (PF14411) domains, respectively. The C-terminal nuclease domains from E. coli NC101 and 3006 cleave tRNAAsp/tRNAGlu and tRNAIle, respectively. The nuclease domain from E. coli EC869 is a Zn2+-dependent DNase, and the activity of the Dickeya dadantii 3937 toxin is unknown. N-terminal domains are labeled according to their putative membrane receptors. The pretoxin-VENN domain and the conserved VENN motif are also depicted. (C) CDI competitions. E. coli target cells were cocultured with the indicated CDI inhibitors. Average target-cell counts (±SEM) are presented for three independent experiments. Where indicated, target cells were provided with the cognate cdiI immunity gene.