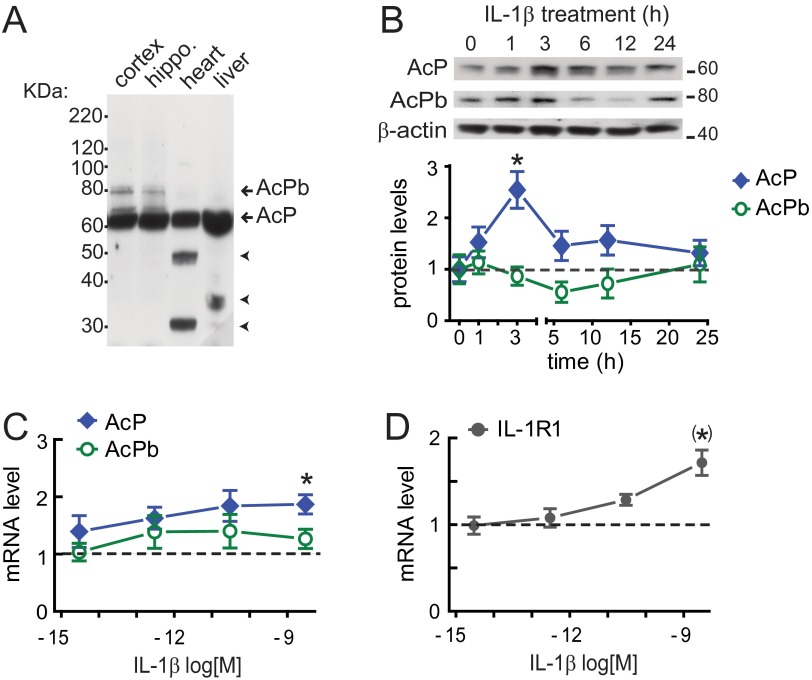
Fig. S1.
AcP induction by IL-1β is time- and concentration-dependent. (A) CNS-restricted expression of AcPb. AcP (∼62 KDa) and AcPb (∼80 KDa) detection by Western blot (full-length blot) is shown. Unidentified proteins (arrowheads) were detected in heart and liver. (B) AcP and AcPb by Western blotting in cultured hippocampal neurons (5–7 DIV) treated with 3 nM IL-1β for the indicated times; β-actin served as loading control. AcP and AcPb densitometry values were quantified at each time point and normalized to vehicle-treated cells (time = 0). *P < 0.05 [AcP vs. control; ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 6 per group; six independent experiments (neurons from different embryo litters)]. (C and D) mRNA levels in neurons treated with IL-1β (3 fM to 3 nM; 100-fold increase) for 3 h; shown are AcP (C; n = 7), AcPb (C; n = 5), and IL-1R1 (D; n = 7), with results from seven independent experiments. Values were normalized to vehicle-treated cells (dotted line), and GAPDH was used as internal control. *P < 0.05 (AcP vs. control); (*)P < 0.01 (IL-1R1 vs. control) (Kruskal–Wallis, Dunn post hoc test). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.