Fig. 4.
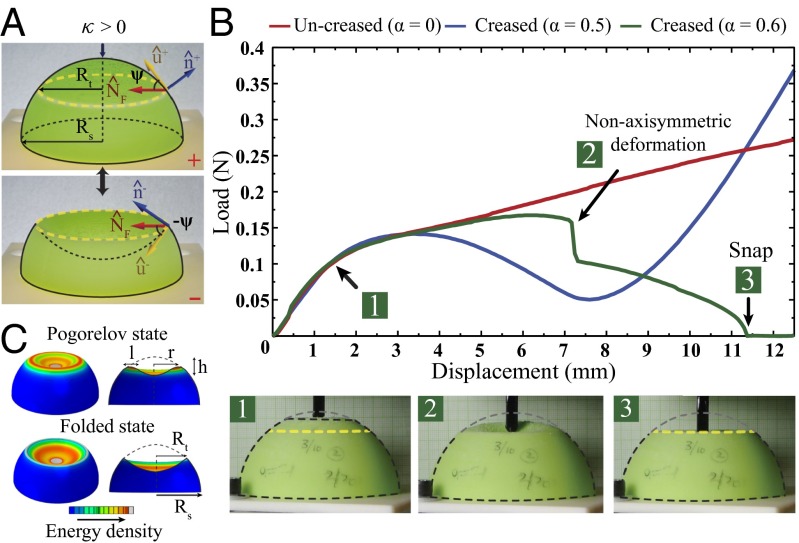
Folding of spheres (). (A) Spherical shell of thickness t, radius , and a crease radius in bistable states (+, −). Vectors (, and ) and parameters (, and ψ) used in this study are overlaid on the experimental sample. (B) Spherical shells with crease radius (red), 0.5 (blue), and 0.6 (green), and over all radius . For the smaller value of α, no stable snap is observed indicating monostability, whereas for larger value of α a nonaxisymmetric deformation, followed by a stable snap, occurs under indentation (Movie S3). (C) Schematics for the Pogorelov state of a deformed spherical shell, with representative ridge (of size ) at a radius r; and the folded state of a creased spherical shell (radius ), with a crease radius .