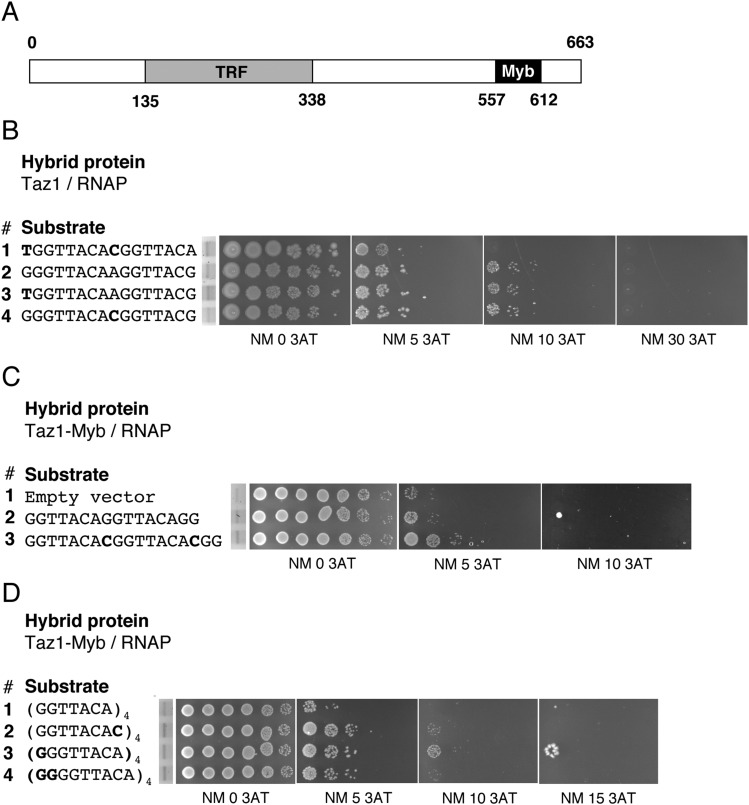
Fig. S8.
Taz1–telomere repeat interaction. (A) Schematic of Taz1 structure. Myb, Myb/SANT domain; TRF, Telomere repeat binding factor domain, dimerization domain. Amino acid numbers are indicated. (B) Bacterial one-hybrid activity assay. Shown are interactions between Taz1/RNAP and telomeric repeats as assayed by growth of 10-fold dilution series on 0, 5, 10, and 30 mM 3-aminotriazole. DNA sequences are depicted with relevant mutations in bold. Dilution series preceded by EtBr-stained gels demonstrate equivalent substrate levels. (C) Bacterial one-hybrid activity assay. Shown are interactions between Taz1-Myb/RNAP (amino acids 557–612) and telomeric repeats as assayed by growth of 10-fold dilution series in 0, 5, 10, and 30 mM 3-aminotriazole. Taz1-Myb DNA binding domain was used to avoid protein dimerization, which interferes with the one-hybrid assay. DNA sequences are depicted with relevant mutations in bold. Dilution series preceded by EtBr-stained gels demonstrate equivalent substrate levels. (D) Taz1-Myb domain binding to four direct repeats of the indicted sequences. (D, Left) The same as described in C, except that four telomeric repeat tracts were assayed at 0, 5, 10, and 15 mM 3AT.