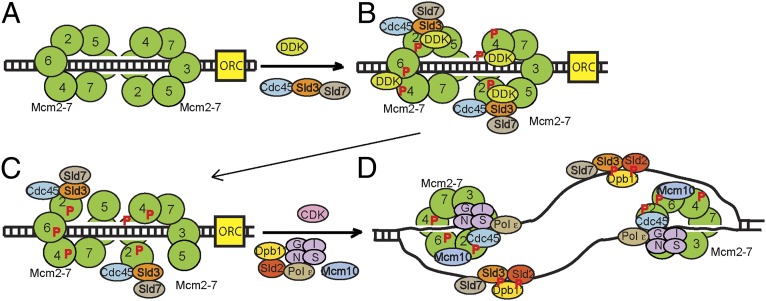
Fig. 4.
Model for the initiation of DNA replication. (A) Mcm2-7 loads as double hexamer to encircle dsDNA during late M and G1 phases. (B) In S phase, Sld3, along with Sld7, recruits Cdc45 to Mcm2-7. Sld3, while bound to Mcm2-7, substantially stimulates DDK phosphorylation of Mcm2. DDK also phosphorylates Mcm4 and Mcm6. Sld3 also blocks the premature interaction between GINS and Mcm2-7. (C) Once Mcm2 is phosphorylated by DDK, the interaction between Mcm2 and Mcm5 weakens, allowing single-strand extrusion from the central channel of Mcm2-7 (origin melting). (D) Sld3-Sld2-Dpb11 form a CDK-dependent ternary complex in S phase. Once the origin is melted, Sld3-Sld2-Dpb11 is released from Mcm2-7, because Sld3-Sld2-Dpb11 binds preferentially to ssDNA. The sequestration of Sld3-Sld2-Dpb11 onto ssDNA allows GINS to engage with Cdc45-Mcm2-7, and the CMG helicase is assembled and activated for unwinding.