FIGURE 7.
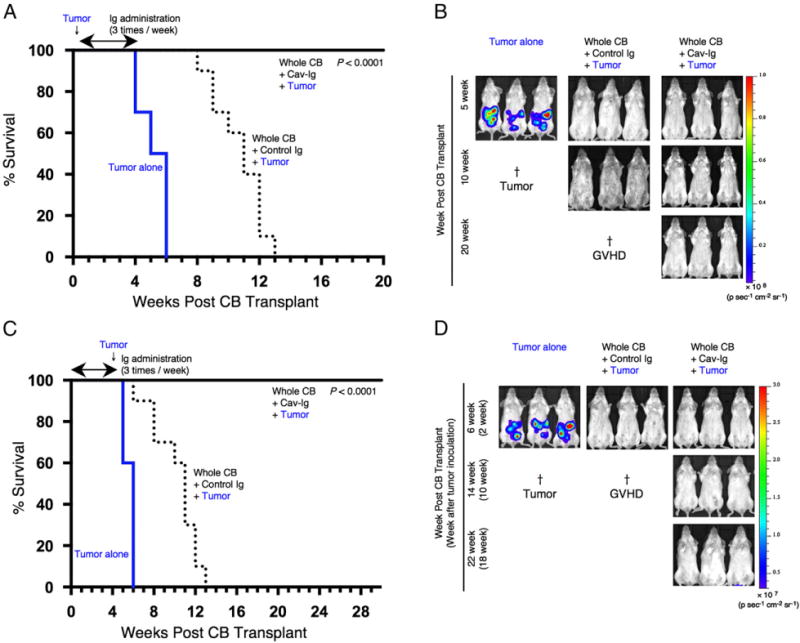
Cav-Ig preserves GVL effect. (A) NOG mice were irradiated at sublethal dose (200 cGy) and the next day were inoculated with 1 × 104 A20-luc cells via tail vein, and then were transplanted the following day with 1 × 107 MNCs isolated from HuCB. Cav-Ig or control Ig (each 100 μg/dose) was administered i.p. thrice per week, beginning at day +1 after transplantation until day +28. Overall survival is depicted from cumulative results from three independent experiments (for each, n = 10). p < 0.0001 versus recipients of control Ig by log-rank test. (B) In vivo bioluminescence imaging was performed at the indicated time points after treatment, as described in (A). Representative mice are shown. Ruffled fur consistent with skin GVHD is shown in recipients of control Ig group at 10 wk posttransplant (middle panel). †Death of all mice in the group of tumor alone or control Ig groups. (C) Sublethally irradiated NOG mice were transplanted with MNCs isolated from HuCB. Cav-Ig or control Ig was administered i.p. thrice per week, beginning at day +1 after transplantation until day +28. A total of 1 × 105 A20-luc cells was inoculated via tail vein on day +28 posttransplantation. Overall survival is depicted from cumulative results from three independent experiments (for each, n = 10). p < 0.0001 versus recipients of control Ig by log-rank test. (D) In vivo bioluminescence imaging was performed at the indicated time points after treatment, as described in (C). Representative mice are shown. Slightly ruffled fur consistent with skin GVHD is shown in recipients of control Ig group at 6 wk posttransplant (middle panel). †Death of all mice in the group of tumor alone or control Ig groups.
